Table of Content
Virtual reality (VR) emulates a real or imagined world through computer-generated environments. These artificial settings, crafted with software, aim to immerse users fully by replicating a realistic experience. Some instances go beyond mere representation, allowing users to suspend disbelief and perceive the virtual environment authentically as accurate.
The human brain relies heavily on vision to perceive the world, so virtual reality (VR) technology primarily focuses on accurately simulating sight. For functional VR, we mainly need two components. The first component is the wearables, which give environmental information to the computer and feed virtual information to the user. The second component programs computer software that can generate these environments.
Sophisticated software algorithms are used to create two-dimensional images and videos that feel three-dimensional. Once these visuals are rendered and processed, they are sent to a screen in the VR headset, blocking out information from the real world and displaying the virtual world.
The VR headset has two autofocus lenses that can adapt to eye movements and position. This enables the computer to monitor and modify the VR display to correspond with your physical movements. Additionally, algorithms create a stereo sound projected onto the headset in sync with the images. The headset and hand controls incorporate motion and pressure sensors that relay feedback to the computer. The computer dynamically adjusts the 3D environment in response to your physical actions. Technological advancements are pushing the boundaries by striving to replicate every sensory experience, encompassing touch, smell, and even taste.
In virtual reality (VR), hardware and software collaborate to craft immersive encounters that effectively deceive the brain and senses. Software is responsible for shaping the virtual environment, while hardware facilitates sensory experiences such as sound, touch, smell, or heat intensity.
Wearable devices
Science fiction movies have always been a source of inspiration for future technologies. But the truth is that while we are getting closer to some of the things they show, there are other things that we still need to work on. The first thing you need to enter a virtual space is a device that will engage your senses and make the virtual world seem real.
You might be thinking about VR headsets like Oculus Rift or HTC Vive. But these devices are not enough. You’ll also need an audio system (like headphones) and hand controllers to interact with the virtual world.

Software
VR software is the backbone of VR content. It manages all the data from the user and environmental sensors and then generates a virtual environment in real-time. VR software has a big job: it must deliver content from the cloud and internet, manage all connected devices, analyze incoming data from user and environmental sensors, and generate a virtual environment in real time. The success of a VR experience depends on how well the software manages the content. It’s also essential for VR software to manage all of this information because, without management, the consequences become dire, and it may affect the user’s well-being.
A virtual world generator is a software development kit that provides the basic programs, drivers, data, and graphic-rendering libraries. The virtual world generator is a 3D modeling environment for creating virtual worlds. It has been created with the help of different types of software development kits.
To create VR, developers employ a variety of software. They include visualisation software, content management, game engines, social platforms, and training simulators. They also contain VR software development kits.
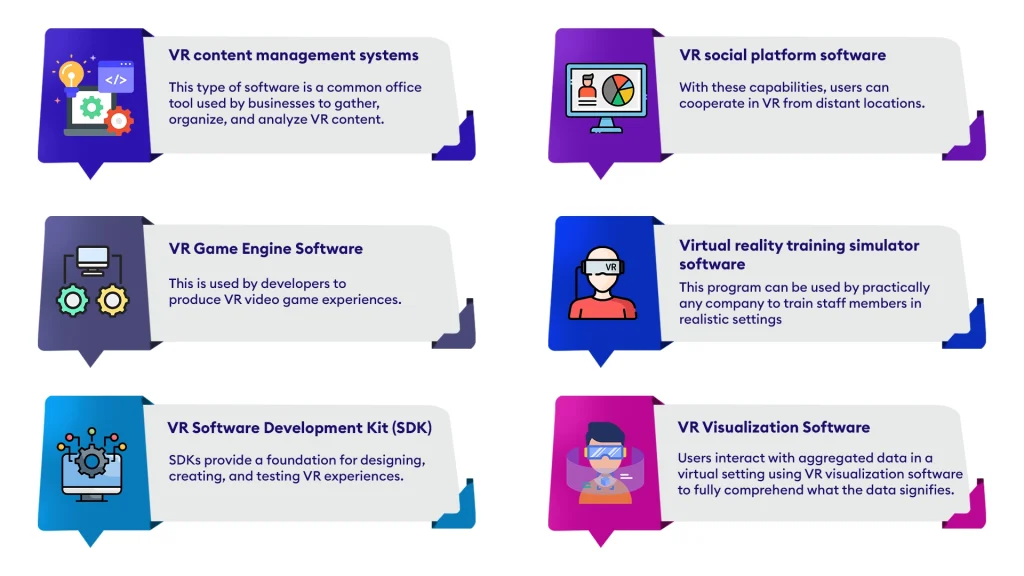
What can you do with VR?
In the past, VR was mainly used for gaming, but now it is used for other things such as education, healthcare, and tourism. The global (VR) Virtual Reality Gaming Market is Set to Reach $90.7 billion by 2026 at a 31.4% CAGR.
With the help of virtual reality, homebuyers can explore the properties they are interested in buying more immersively. This enhances their experience and gives them an idea of what it would be like to live there.
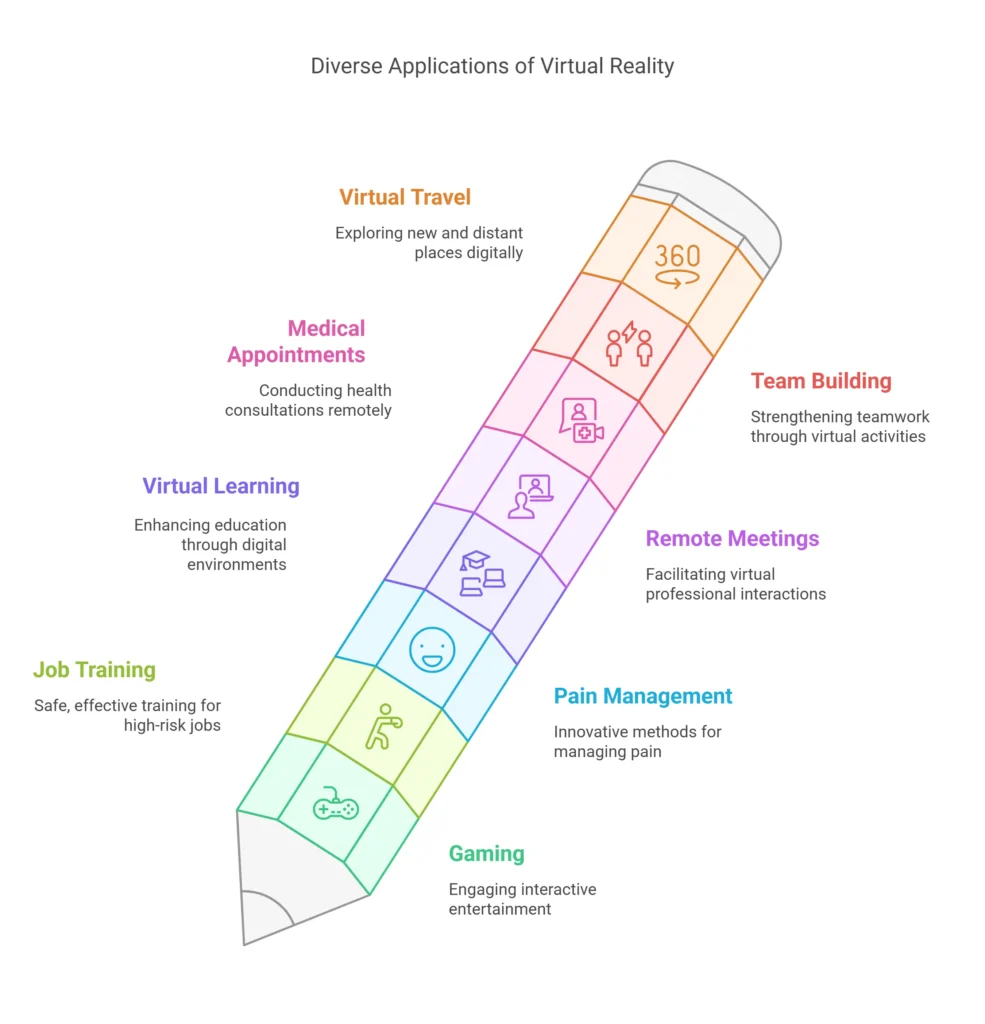
Virtual reality has the potential to serve a variety of purposes beyond its current applications. Both in the present and the future, virtual reality can be utilized for the following reasons:
- Gaming
- Job training: Virtual reality provides a safe, effective, and cost-efficient method for training individuals in high-risk or specialized occupations, such as firefighters, EMTs, police officers, soldiers, Pilots, surgeons, or medical staff. 1
- Pain management
- Virtual learning in classrooms
- Attending work meetings remotely
- Conducting medical appointments, including therapy sessions
- Team building exercises Virtual travel, including to extraterrestrial locations (although currently limited to the best virtual space exhibits)
- Socializing
- Online dating
- Virtual shopping
- Exploring museums and historical events
The term “metaverse” was coined by Neal Stephenson in his 1992 novel “Snow Crash.” It has been used to describe a future virtual world where people can interact with each other through avatars, items, and locations. The virtual world is also called cyberspace, the matrix, or the internet. The metaverse is an infinite space hosted by millions of servers worldwide. There are many ways to access it, such as VR headsets, AR glasses, and smartphones.
The future of space tourism may include virtual reality experiences. While currently, there are 3D virtual tours on platforms such as YouTube, space tourism may also involve virtual reality simulations in the future. This means that individuals could potentially experience space travel through a VR simulation without actual space travel’s associated risks and costs.
The future of virtual reality will bring about significant changes compared to the present, with advancements in technology making new possibilities and experiences accessible. While there are numerous other virtual reality applications not mentioned in this list, they will become possible with future technological developments.
VR Accessories
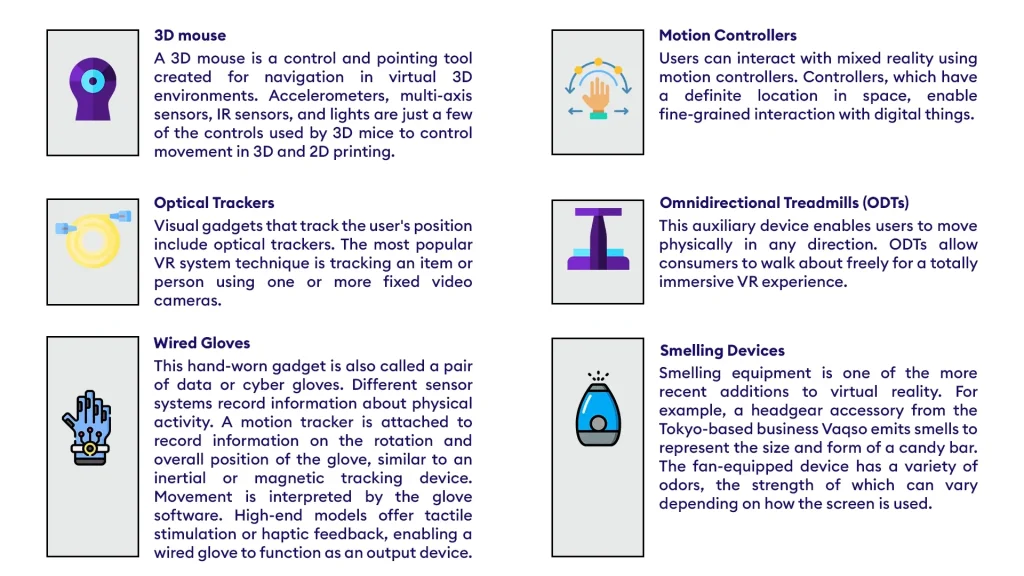
Virtual reality (VR) accessories are hardware items that support VR technology. The development of new gadgets to enhance the immersive experience is ongoing. Modern accessories include 3D mice, optical trackers, wired gloves, motion controllers, bodysuits, treadmills, and even smelling gadgets.
The accessories in use in today’s market could be cited as:
As mentioned in our introductory article for VR, the future of VR is exciting and filled with endless possibilities. From exploring the vast expanses of the metaverse to virtually visiting far-off destinations, VR offers unique and exciting experiences that were once only imaginable.
- Techtarget: www.techtarget.com[↩]
- Marxentlabs: www.marxentlabs.co[↩]


