Have you ever wondered what owning an authentic art piece in a virtual world would be like?
Questions like “How would you claim ownership?” or “How would you validate your ownership?” would immediately pop into your mind. The concept of ownership and authenticity in the digital world is complex. In the physical world, claiming ownership of a product by simply holding it is easy. However, claiming ownership of virtually anything that can be created is easy in the virtual world. NFTs solve this problem with an immutable ledger that cannot be changed. This means that if one claims ownership of an item on the blockchain, they are, in fact, the legitimate owner and can prove this by providing their ID or other proof of identification.
The idea of a tokenized digital representation of a physical item has been in existence for decades. In NFTs, ownership and authenticity are validated by a decentralized system that is not controlled by any entity. NFTs are being used to represent ownership and authenticity in many ways. One example is in the world of art. Unlike paintings that can be copied and reproduced, NFTs cannot be duplicated without the original owner’s consent. The concept of NFT came to life in 2014 when digital artist Kevin McCoy minted the first NFT called Quantum. Quantum is a clip of a pixelated octagon filled with different shapes, which was initially sold for $4. 1
What are NFTs?
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, are a kind of digital asset that signify ownership or provide confirmation of the authenticity of a special good or piece of material, such as a piece of art, some music, a movie, or even a tweet. NFTs are not interchangeable with one another, unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, as each one is distinct and has a different value. They are produced utilizing blockchain technology, guaranteeing legitimacy and offering an open ownership history. Although these have grown in popularity recently, and some have reached millions of dollars at online auctions, their applications and potential effects on the art and entertainment sectors are yet to be seen.
Although these were first minted in 2014, it was not until 2021 that NFTs became a considerable investment. 2
Fungible vs. Non-Fungible Tokens
The two categories of digital assets that saw the fastest growth recently are fungible and non-fungible tokens. Fungible tokens, like cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are interchangeable and have a fixed value. These tokens are exchangeable because they share the same qualities. Non-fungible tokens, on the other hand, are exclusive and cannot be used interchangeably. Each non-fungible token stands in for a particular object, whether a work of digital art or a collectible. These unique tokens can’t be duplicated or divided since they are one of a kind. Non-fungible tokens are generally utilized for ownership and authenticity verification of individual digital assets, whereas fungible tokens are employed as trade.
Unique Attributes
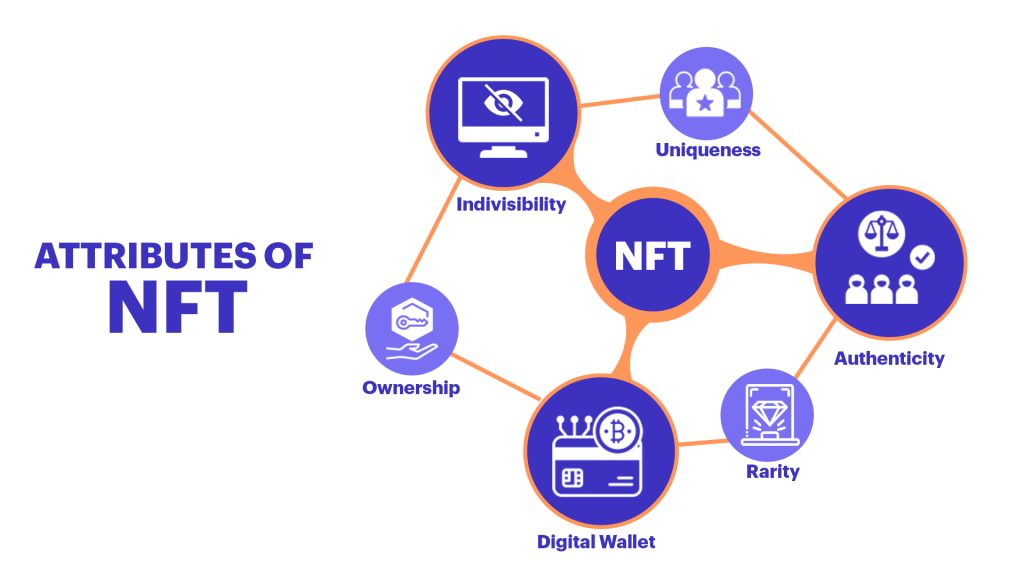
NFTs have six unique attributes that define them. These include uniqueness, indivisibility, transparency, ownership, interoperability, and Scarcity.
- Uniqueness: These are unique. There cannot be identical NFTs, just like fingerprints.
- Indivisibility: These cannot be divided or separated.
- Transparency: These are transparent. Whenever a transaction is made, it is recorded on the blockchain.
- Ownership: All these are live in an account created by the original creator, who can control the account’s settings and privacy. The owner can transfer the version with the NFT to another person.
- Interoperability: These can be sold, purchased, or traded across various authorized platforms.
- Scarcity: NFTs are high in demand, hence the increased number for value. 3
What is the future of NFTs?
Many believe that these could have a bright future since they provide new options for investors, collectors, and creators. These have already transformed the art market by enabling artists to sell digital artwork as unique, one-of-a-kind items. NFTs have also entered the gaming sector, where they may stand for certain in-game goods or even whole virtual worlds. These can also confirm the ownership and legitimacy of tangible assets, such as luxury items or real estate. These are anticipated to expand as blockchain technology develops, with possible applications in fields like ticketing, identity verification, and more.
However, tackling issues like high transaction costs, environmental effects, and market instability is also crucial to the future of NFTs. Overall, the potential for NFTs is vast, and their future will likely be shaped by continued innovation and experimentation. 4
- Gfinityesports: www.gfinityesports.com[↩]
- nftnow: https://nftnow.com[↩]
- Nansen: www.nansen.ai[↩]
- Seekingalpha: seekingalpha.com[↩]


