Finance… the backbone of the global economy, provides the means for individuals, businesses, and governments to manage their financial resources. The financial system, which includes banks, insurance companies, and other financial institutions, provides services such as lending, borrowing, and risk management and facilitates the flow of capital throughout the economy. Without a well-functioning financial system, economic growth and development would be hindered.
The traditional financial system is built around a centralized structure, allowing central banks and other institutions to govern our financial system. For example, when obtaining a bank loan or buying stocks, we must go through a slew of middlemen paying transaction fees at every stage. Decentralized finance aims to remove these intermediaries and take a more democratic approach to finance through blockchain technology.
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and How Does It Work?
DeFi is an umbrella term used to describe financial services and applications built on top of blockchains, with the aim of disempowering traditional financial intermediaries such as banks. In other words, decentralized finance is a financial system that enables peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a central governing authority.
As mentioned above, decentralized finance applications are built using the same blockchain technology as cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum. Since the blockchain is an immutable, distributed, and public ledger, it allows for greater transparency and security. Typically, DeFi is accessed through software called dApps (decentralized apps), and these applications are mainly built on the Ethereum blockchain. Additionally, DeFi protocols use smart contracts, which are essentially self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code.
Exploring the Benefits of Decentralized Finance: Financial Inclusion and Innovation
One of the core principles of DeFi is financial inclusion, as anyone with an internet connection can access its services. On the contrary, traditional financial services require specific prerequisites such as credit scores, which results in certain individuals being barred or restricted from obtaining financial services. In addition, DeFi has the potential to transcend geographical borders and provide global access to finance.
Since decentralized finance removes middlemen, transaction fees are significantly lower. Another benefit is higher yields. To understand this, let’s look at the following scenario.
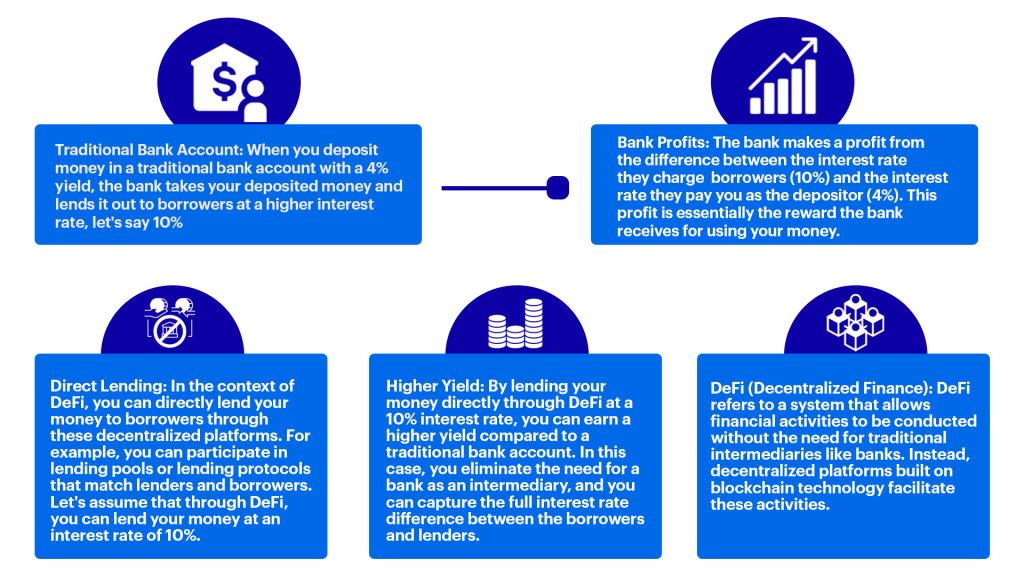
Traditional finance is held together by decades-old infrastructure and processes, which severely limits its ability to innovate. DeFi paves the way for more innovation in the finance sector as it creates new financial products and services beyond the scope of traditional financial systems.
Developments in Decentralized Finance & Their Impact on Traditional Banking Models
The development in the field of DeFi can be clearly seen by analyzing the TVL (Total value locked – a measure of DeFi transaction value).
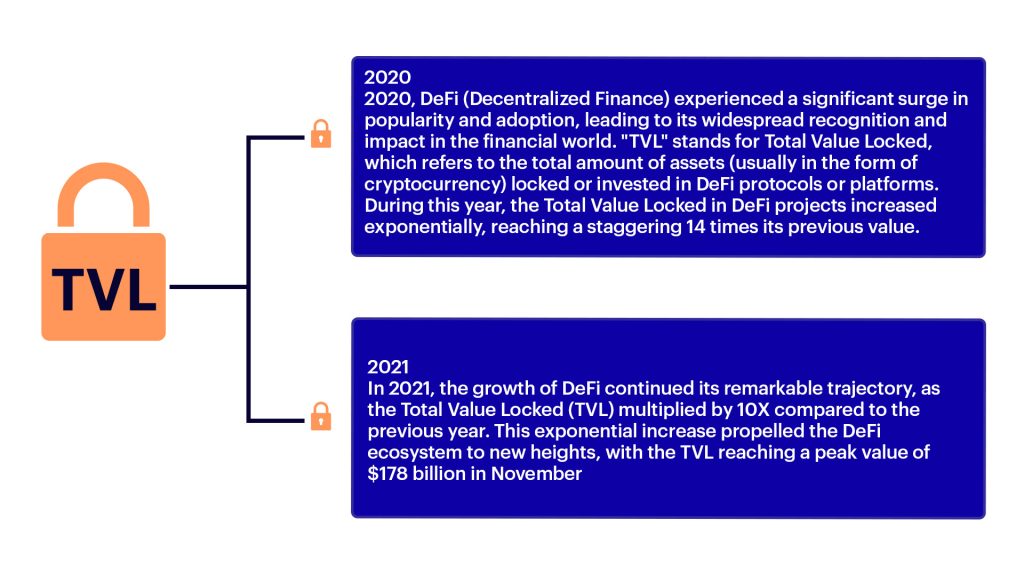
At a glance, DeFi seems superior to its traditional counterpart, with lower transaction fees, greater financial inclusion, higher yields, and more transparency. However, since this is a relatively new and untested technology, banks may have concerns regarding its security and stability. Additionally, traditional banks may view them as a threat to their current business model and may resist adoption. Despite this, DeFi is expected to continue growing, and traditional banks will need to adapt to remain competitive.1
Exploring The Benefits of DeFi for Traditional Banking & Businesses
Traditional banks and businesses have much to gain by adopting DeFi technology. Let’s examine some of these benefits below:
- Fast and Reliable Transactions: Since smart contracts facilitate transactions, human error and manual validation are eliminated, thus reducing transaction processing time and increasing transaction reliability.
- Greater Accessibility: DeFi markets are open 24/7 and are accessible through an internet connection from anywhere in the world. This makes it a more convenient option for businesses and entities in different time zones than the market they operate in.
- Higher Transparency and Security: DeFi applications are built on public blockchains, making them more transparent and tamper-proof. Further, the status of the DeFi protocols can be viewed in real-time, increasing public faith in financial institutions.
- Availability of New Financial Products: DeFi can open up new business opportunities to develop innovative financial products and services. An ideal example of this would be yield farming, which was previously only available to wealthy individuals and large institutions and is now open to anyone who owns cryptocurrency.
- Increased efficiency: DeFi can automate specific processes, such as loan servicing, through the use of smart contracts, which in turn reduces processing time, resulting in cost and time savings.
The Challenges of Adopting Decentralized Finance in a Traditional Financial Model
DeFi sounds promising, but in our current financial landscape, it faces many challenges before it can be widely adopted. A few of those challenges are:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Since most technologies associated with DeFi are new, they still need to be regulated. This can prove challenging to traditional financial systems when adopting it.
- Security Risks: Although DeFi is built on secure blockchain technology, there are still potential security risks, such as hacking and fraud.
- Interoperability Issues: Current DeFi protocols and platforms often need to be interoperable with each other, making it difficult to connect different systems and networks.
- Scalability: Some DeFi protocols were not built to handle many transactions and can lead to performance issues when trying to scale.
- Non-User-Friendly: DeFi platforms may not be as user-friendly as traditional financial systems, making it difficult for some people to use them.
- Liquidity: Some DeFi protocols may need more liquidity, which makes it challenging to buy and sell assets.
How DeFi Can Help Create a More Equitable Financial System?
The first step in creating a more equitable financial system is reducing barriers to entry. DeFi is a pioneer in this regard, requiring only an internet connection while disregarding factors such as creditworthiness or location.
Further, DeFi systems are run by algorithms and AI (Artificial Intelligence) models, which do not require human intervention; therefore, market conditions such as interest rates depend only on supply and demand, unlike traditional finance, where central banks decide market rates.
DeFi also can democratize finance by giving users more control over their financial data and assets; this, in turn, will reduce the power of centralized authorities.
What Are the Different Types of DeFi Solutions?
Decentralized exchanges
A Decentralized exchange, more commonly known as a “Dex”, allows users to trade digital assets in a peer-to-peer environment without a centralized authority. This is done so by utilizing a decentralized order book. As a result, all the assets being traded on the exchange are in the custody of the users and not the exchange. Further, any major decision regarding the dex itself is made with the participation of all platform participants.
Stablecoins
These cryptocurrencies are pegged to the value of a fiat currency or other assets, such as gold, to provide stability and reduce volatility. Non-custodial stablecoins function as DeFi services, while custodial stablecoins are centralized and can be incorporated into DeFi services.
Lending/borrowing platforms
These platforms allow users to lend and borrow various cryptocurrencies, such as bitcoin, without a financial intermediary, through smart contracts to specify details such as repayment date, interest rate etc.
DeFi insurance
The DeFi space contains various risks that require new types of insurance. These services offer a more democratized version of insurance. The users trade the payment of a guaranteed small premium for the possibility of collecting a large payout in the event of a covered scenario while the liquidity providers earn interest. 2
What Are the Security Risks Involved in Using a DeFi App or Protocol?
DeFi, like any new technology, carries some risks. As a result, users must conduct thorough research and due diligence on the DeFi apps and protocols, and they must always remain vigilant of potential security risks.
Now let us look at some of the risks DeFi poses:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts, which serve as the backbone for many DeFi protocols, may contain bugs or vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit.
- Phishing Scams: DeFi apps and protocols are popular targets for phishing scams, where hackers use social engineering tactics to trick users into revealing their private keys or seed phrases.
- Liquidity Risks: Some DeFi protocols rely on liquidity pools to function, but if these pools dry up, it can lead to a lack of liquidity and make it difficult for users to exit their positions.
- Oracle Attack: DeFi protocols that rely on Oracle to function can be vulnerable to Oracle manipulation, in which an attacker alters the data feed to execute a malicious action.
- Legal Risks: DeFi protocols operate in a legal grey area, and regulatory changes can significantly impact the value of assets held in these protocols.
Conclusion: How Can We Leverage Decentralized Finance for Enhanced Accessibility and Efficiency?
Traditional finance is built on trust, whereas DeFi is built on code. DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, is an excellent alternative to the traditional Wall Street financial system. It takes many of the principles and features of Bitcoin and builds on them, creating a digital network that has low cost yet offers similar services and features as Wall Street. This can create more open, free, and fair financial markets that are accessible to anyone who wishes to use their services.
- DeFi trends: https://explodingtopics.com/blog/defi-trends[↩]
- blog.1inch.io: https://blog.1inch.io/types-of-defi-their-pros-and-cons/[↩]


