Table of Content
The verification of ownership of any physical or digital asset is essential for the legitimacy of financial and non-financial transactions. Conventionally, the authentication process for these assets has been documented on paper or digitalized into a central database, which is often inefficient and exposes them to fraudulent documentation processes. NFTs have given creators the opportunity to signify the ownership of virtual assets. These are blockchain-based tokens that represent different forms of unique digital collectibles, such as art and media. 1
Utilizing a structured approach, metadata is used to define the unique features of various kinds of NFTs. A comprehensive synopsis of different types of NFTs, such as digital artwork, audio files, photographs, and animations, is included in the metadata. For instance, level, rarity, and quality are a few attributes defined by metadata with respect to an NFT game card. 2
Metadata is utilized in the development process of an NFT. It is important to showcase the unique attributes of each and every NFT to increase its desirability and value. Creators must use differentiating tactics to market a compelling representation of their tokens.
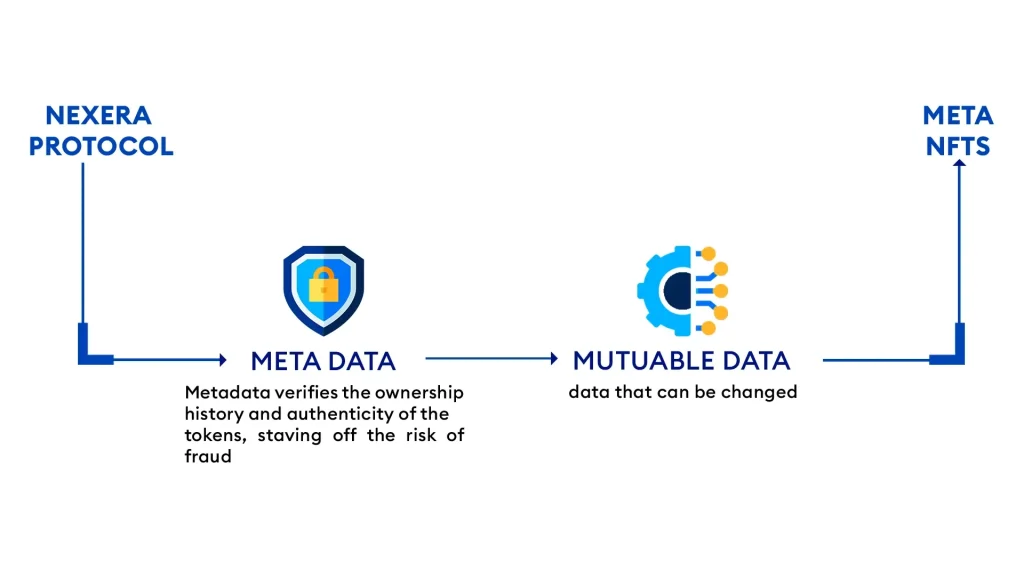
Metadata verifies the ownership history and authenticity of the tokens, staving off the risk of fraud. As the market for NFTs becomes more and more accepted by regulators and the general public, the importance of metadata is set to increase at an exponential rate. 3
What are Meta NFTs?
The Nexera Protocol was introduced by the AllianceBlock as a stepping stone for the next generation of NFTs. Abiding by the current regulations and standards, the Allianceblock created a mutable and composable NFT known as Meta NFT. Comprising both metadata and mutable data, meta NFTs are defined to be the third generation of tokens. Meta NFTs have the added advantage of comprising both types of data, which in turn leads to a greater dynamic evolvement with the changing digital regulations and properties.
The Metadata are stored independently from each NFT. 4 They exist as separate objects at different locations of the network. There are two major ways of storing metadata; On-Chain Metadata and Off-Chain Metadata. If the NFT description lives on the blockchain, it is interpreted as on-chain metadata. This encompasses both metadata and smart contract details. Since the metadata, smart contracts, and tokens are stored on the blockchain, there is no requirement for relying on external storage systems.
Comparatively, as the name suggests, off-chain metadata is stored externally from the blockchain. 5 The third generation of on-chain meta NFTs are mutable storages that can connect and interact with on-chain and off-chain data entities. As the legitimacy of NFTs and their standards are accepted by regulators and traders, the meta NFTs can overcome obstacles and developers can add more useful attributes to every token in the market.
Financially, meta NFTs can be used to represent asset-backed loans, investments and accounts comprising properties that are mutable depending on on-chain and off-chain data. The above-mentioned financial trades can be stored on a single meta NFT. 6
Creation of Meta NFTs
The first generation of NFTs included on-chain identifiers that were attached to a distinct wallet. over time, a few new properties were added to enhance the capabilities to cater to the evolving market. Information about transfers is recorded within the NFT. Unfortunately, due to the inherent strict standards, NFTs are not able to evolve once it has been minted.
Off-chain capabilities were introduced as a part of the advancement process from the 1st generation to the 2nd generation of NFTs. Hence, it supports both on-chain and off-chain metadata. Each NFT is a unique object representing a digital or physical asset, where the linked metadata is stored on-chain or off-chain that can verify the proof of true ownership.
These include art illustrations as seen during the NFT boom in 2021. Also, the 2nd generation of NFTs has been utilized by developers as a way of paying royalty fees for artists and event ticketing. The dynamic market of NFTs has integrated both the 1st and 2nd generation features to create a comprehensive token, however, the unstructured approach of storing metadata on-chain and off-chain, and the creation of non-interoperable NFT standards developed the need for an advanced new version of NFTs. 6
Blockchain interoperability feature enables different blockchain networks to integrate, communicate and share data among a set of distinct chains. Interoperability is essential for the creation of a sustainable Web3 ecosystem where information can be seamlessly shared among chains. 7
The Nexera protocol addresses the issue of metadata and interoperability with the development of 3rd generation NFT standards. Fractured metadata and non-interoperability paved the way for Meta NFTs. Comprising mutable data and metadata, MetaNFTs have the capacity to interact with both on-chain and off-chain systems, while updating necessary changes in properties due to parameter fluctuations alerted by external sources.
The various properties and features can be accumulated and attached over a period utilizing the 3rd generation standards. The objective of the Nexera protocol is to authenticate the true ownership, provide custody of the NFT, and the metadata under it to the user.
In technical terms, MetaNFTs are user-centric repositories providing on-chain solutions for reserving data within the boundaries of the NFT identifier. The control of mutables and metadata will be within the jurisdiction of the user. Smart contracts and attached properties can interchange with those specific information. Since the interaction with third-party external sources is eliminated, the user can govern the processes of storing and accessing data. This is identified to be the beginning of the road towards a truly decentralized NFT market space. 6
Buying and Selling Meta NFTs
The digital platform developed for buying and selling NFTs can be identified as an NFT marketplace. The marketplace allows creators and collectors to communicate and perform transactions in the NFT space. Discoverability, transfer of ownership, rarity and provenance are key functions associated with the platforms other than buying and selling NFTs. Smart contracts are incorporated within the marketplace to ensure the seamless functioning of pre-developed protocols. The completion of each protocol requirement provides a solid foundation for trades and transactions. 8
OpenSea is crowned as the most popular MetaNFT marketplace accompanying a variety of tokens. “Lazy Minting” is utilized to streamline the development process of NFTs. The existence of various types of tokens and the user-friendly interface have added more value, despite the arguable high brokerage fee. 8
Rarible is also a popular destination for NFT trades; however, unlike OpenSea it is a decentralized marketplace. Creators and collectors have the opportunity to perform transactions without interference from other intermediaries. The community-driven concept has attracted artists and collectors who are keen to have true ownership and control over NFT projects. 9 Each marketplace acquires a transaction fee from the users as a way of monetizing the NFT space.
Most Expensive Meta NFTs
The concept of non-fungible tokens is being appreciated more by the crypto community due to the current economic and ecological conditions around the world. The NFT market created a new segment of creators and collectors with an increase in value for digital art.
An unprecedented number of transactions have gone through in recent years, breaking record after record and flowing billions of US dollars in and out of the NFT market. The introduction of decentralized assets in the blockchain arena has expanded the growth capacity and monetary value of NFTs. 10 Collectors are inclined to spend more on scarce digital assets because of their uniqueness and rarity; hence, the ability to charge an exclusive price is high.
“Merge,” created by the digital artist ‘pak’, has been recorded as the highest ever-sold NFT on the Nifty Gateway platform in December 2021.
It was able to fetch a record-breaking price of US$91.8 million with 28.983 collectors snapping up 312,686 total units of NFTs. “The First 5000 Days,” designed by Mike Beeple Winkelmann, consists of more than 5000 pieces combined together once per day since May 2007. The digital artwork was sold for US$69.3 million at Cristie’s Auction Digital Art House in 2021.
The mainstream adoption of NFTs has not yet occurred; however, NFTs as a vehicle of expression are racing towards global acceptance. 11
Value Proposition of Meta NFTs
Through the introduction of MetaNFTs, the digital landscape for creators has expanded to new heights, enabling borderless interaction in a decentralized ecosystem where buyers and sellers can trade tokens attached to whatever their creative minds can imagine. The decentralized environment allows fair interaction and communication between creators and collectors. Third-party barriers have also been removed due to the uniqueness of MetaNFTs. The purchasing and distribution process of such Non-Fungible Tokens are under the direct supervision of the owner so that all the movements can be tracked with each transaction. In today’s age, some NFTs are designed to accumulate a royalty fee for the original creator from each trade. 12
Furthermore, the competitive environment in NFT marketplaces has given the NFT community opportunities to choose from different segments across all the platforms, enabling the foundation of differentiated products. More options for buying, selling, and setting prices for MetaNFTs are in existence now. Also, due to the decentralized ecosystem, the presence of NFTs is verified and supported by thousands of nodes around the globe, without the interference of governments and other authorities. Since NFTs are located in distributed blockchain networks, the assets linked to each NFTs are secured and out of reach of government seizure. 12
The occupation of artistry is considered to be an unstable way of generating income by the majority of the general public. For a traditional artist, waiting for sales and commissions is the normal route to making a living; however, it is not as scalable as NFTs. Artists now have the opportunity to raise funds while the artwork is still in progress as a method of fundraising. A specific portion of income can be supplemented while at work for NFT creators. 12
Environmental Impact
As more and more organizations develop sustainable policies towards creating products and services, the pressure from governments and the public is notable concerning the construction process of MetaNFTs.
A significant proportion of energy is utilized for the creation and transactions of NFTs. Robust computational power is required for the process of minting. The need for such power stems from the underlying blockchain network, supplementing the consensus mechanism of PoW. The algorithms used under PoW are high-energy-consuming software. The expansion of the MetaNFT market has signified the environmental impact among regulatory institutions and the cryptocommunity. 13
The implementation of an alternative consensus mechanism known as PoS has been able to reduce the carbon footprint of NFTs. This mechanism requires users to verify the ownership of several coins to authenticate transactions. Hence, energy consumption is reduced significantly due to low computational requirements. Developers are also trying to use renewable energy sources for the existence of the blockchain ecosystem. Carbon offset programs are defined as projects that are implemented to balance the energy consumed with eco-friendly initiatives. These programs are also being used as a way of laying the foundation for sustainable practices within the MetaNFT space. 13
The Process of Minting
The process of uploading a digital file, such as art or audio clips onto the blockchain can be classified as minting MetaNFTs.
The file should be uploaded through a platform that supplements the development of NFTs. The term “non-fungible” stems from the unique identity created through the procedure of minting.
The four general steps of Minting NFTs are as follows,
- Creativity aspect: develop a digital asset
A user must first create a digital asset, which can take the form of a song, image, video, tweet, artwork, and many more. The value of the NFT depends on the uniqueness and creativity of the token.
- Selection aspect: find the suitable blockchain network for the designed token
Users can select any blockchain network to mint the designed NFT. The Ethereum chain has been named the most popular network for trading NFTs due to its advanced smart contract capabilities.
- Selection aspect: select the suitable NFT marketplace
Once the blockchain is selected, the user has to locate the most appropriate marketplace within the chain. For example, Opensea and Rarible are two major marketplaces of Ethereum.
- Minting aspect: upload the digital file
Adding the required metadata, setting an appropriate price, and minting the NFT is part of the final steps. 14

Investment Perspective
As with all investments, NFTs also carry a certain amount of risks and rewards. It is important to understand the gravity of such products before the investment decision has been made. The limited amount of liquidity within the NFT space tends to decrease the return for sellers. A significant proportion of money is utilized for the process of the sale. Also, the unregulated environment around the MetaNFT space creates more legal barriers to its expansion. Traditional investors have not shown adequate support for its sustainability in the future as a method of trade. Legal advice should be taken to identify any potential issues regarding the investment. Furthermore, the demand for the specific MetaNFT determines the price. Demand can fluctuate due to trends, features, uniqueness and other external factors. It is widely seen that some NFTs have been sold for millions of US dollars and others have not even been sold at all. There have been instances where investors have overpaid for a MetaNFT that is overvalued at that time. Despite all the benefits and capabilities of MetaNFTs, it is essential to have a broad understanding of the dynamics within the industry and its underlying risks. 15
- Meta NFTs: https://www.aws.amazon.com[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.finance.yahoo.com[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.oodlestechnologies.com[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.blog.allianceblock.io[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.block.co[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.blog.allianceblock.io[↩][↩][↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.forbes.com[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.blockchain-council.org[↩][↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.linkedin.com[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.metav.rs[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.crypto.com[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://ashurdigital.com[↩][↩][↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.analyticsinsight.net[↩][↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://www.tokenmetrics.com[↩]
- Meta NFTs: https://blockchainmagazine.net[↩]


