- Cryptocurrency Oracles explained
- What is Chainlink and how does it work?
- How Chainlink price feeds are powering DeFi
- Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) explained.
- What is Off-Chain Reporting (OCR) and why is it important?
- Understanding the Benefits of Chainlink Proof of Reserve for Crypto Exchanges
- Challenges faced by Chainlink
Smart contracts have become the forefront of blockchain innovation by ushering in a new era of trust and automation, where transactions are faster, cheaper, and more secure than ever. These self-executing agreements that are coded on blockchains are the building blocks of decentralized applications and platforms.
However, smart contracts suffer from one fatal flaw due to the nature of blockchain. They are inherently closed off and barred from obtaining off-chain data, severely limiting their use. This flaw is known as the Oracle Problem.
In this article, we will explore the world of Chainlink, taking a deep dive into its technology, use cases, and impact on the blockchain industry. We’ll explore the unique features that set Chainlink apart from other Oracle solutions and look at some of the challenges they face as they continue to push the boundaries of decentralized data.
Cryptocurrency Oracles explained
Before diving into Chainlink, we must first understand what an oracle is. Oracles are third-party services that provide external data to smart contracts and decentralized applications. However, using a centralized oracle creates a single point of failure because if the oracle fails or provides inaccurate data, it can compromise the entire system.
So, how is this single point of failure avoided?… By taking a page out of Blockchain 101 and decentralizing oracles. Decentralized oracles remove this single point of failure by distributing the responsibility of data input across multiple nodes in a decentralized network. Using a consensus mechanism, decentralized oracles can ensure data accuracy and mitigate the risk of manipulation or failure by any single node. This way, the decentralized oracle creates a more secure and trustworthy system for smart contracts and decentralized applications.
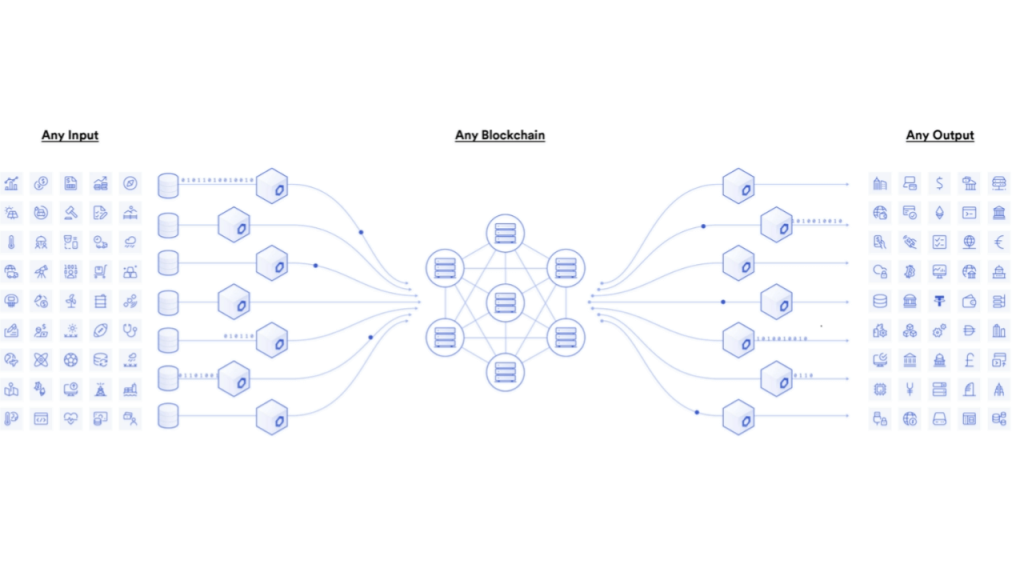
What is Chainlink and how does it work?
It is a decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts to external data sources. It was founded in 2017 by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis and is built on top of the Ethereum blockchain. The purpose of Chainlink is to provide reliable and secure data to smart contracts. It is important to note that chainlink does not have its own chain and runs simultaneously on multiple blockchains.
Chainlink is made up of three main components: the oracle node, the oracle network and the Chainlink network. The nodes are responsible for performing specific tasks, such as data aggregation, computation, and verification. The nodes are then combined together to form an oracle network. Each Oracle network is independent and provides data to its respective user(s). The Chainlink network is the combination of all of these individual oracle networks. This distributed approach ensures that there is no single point of failure, making Chainlink more resilient and secure than traditional centralized Oracle solutions.
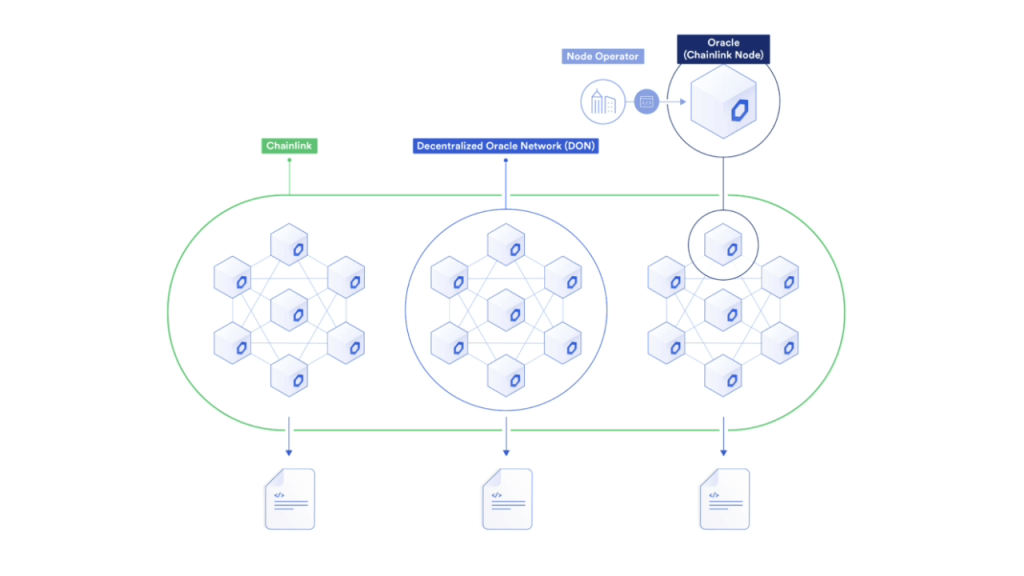
Chainlink also uses a reputation system to ensure that the nodes in the network are trustworthy. Each node is given a reputation score based on its performance and the quality of the data it provides. This reputation score is used to determine which nodes are selected for each Oracle request.
The LINK token is the native cryptocurrency of the Chainlink network and is primarily used to incentivize and pay node operators for providing their services on the decentralized Oracle network. LINK is also used as a collateral asset on the Chainlink network to secure data feeds and other resources. Smart contract developers can use LINK to secure their own data feeds or other network services, adding an extra layer of security and trust.
How Chainlink price feeds are powering DeFi
DeFi has exploded in popularity in the last few years and currently has over $100 billion in TVL (Total Value Locked). DeFi relies on accurate and reliable price feeds to function efficiently.
Chainlink Price Feeds are ‘On-chain reference contracts’ that are automatically updated by decentralized oracle networks (DONs) consisting of Chainlink nodes. Each reference contract stores an asset’s latest and historical price in the form of an exchange rate (e.g. BTC/USD), which smart contracts can then query on demand. Each Chainlink Price Feed runs on a specific blockchain network and regularly updates with fresh data based on predefined parameters. 1
The use of Chainlink price feeds in DeFi creates a more transparent, decentralized, and secure financial ecosystem. By providing accurate and reliable data, Chainlink price feeds ensure that DeFi users can make informed decisions based on up-to-date and trustworthy information. The feeds are highly customizable, enabling developers to create highly specialized applications that cater to specific use cases. As the demand for DeFi applications grows, Chainlink will likely remain a critical player in the industry, providing the infrastructure needed to power the future of decentralized finance.
Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) explained.
The exponential growth of blockchain technology in the past few years has also led to a significant increase in the number of blockchains in the market. While this has opened up a plethora of opportunities for developers, it has also presented them with a significant challenge. The lack of interoperability between different blockchains has made it extremely difficult for developers to build cross-chain applications, hindering cross-chain smart contract development. Cross-chain applications allow users to interact with different blockchains seamlessly, which is crucial for the success of the blockchain ecosystem. However, building them is no easy task. The problem arises because each blockchain operates uniquely, with its own set of rules, protocols, and consensus mechanisms. This makes it challenging for developers to create applications, communicate and operate across different blockchains.
The Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol was introduced by Chainlink to accommodate the growing ecosystem demand for cross-chain solutions. CCIP is an open-sourced standard for cross-chain communication, which provides smart contract developers with a generalized, compute-enabled infrastructure for transferring data and smart contract commands across blockchain networks. CCIP will underpin various cross-chain services, such as the Chainlink Programmable Token Bridge, which will empower users to move their tokens across any blockchain network in a highly secure, scalable, and cost-efficient manner. 2
What is Off-Chain Reporting (OCR) and why is it important?
Scalability has been an issue that has plagued and continues to plague many blockchains. Off-chain Reporting was launched to boost scalability and was arguably the most significant upgrade on Chainlink to date. OCR greatly enhances the data computation efficiency on Chainlink, reducing operating costs by 90%. This major scalability boost will increase the amount of real-world data available on the chain by 1000%, providing greater access to diverse data assets, real-world events, and blockchains. OCR will drive a new wave of smart contract development innovation, allowing developers to service new industries and use cases.
In addition to increasing the amount of data supplied, OCR brings many additional benefits, such as:
- Increased decentralization of Oracle networks
- Higher frequency on-chain oracle updates
- Cost-efficient onboarding of new nodes
- Reduced on-chain network congestion
- Reduced Oracle network latency
These major performance improvements are achieved by allowing chainlink nodes to communicate off-chain. This allows OCR for faster and more accurate aggregation and verification of data. Further, the off-chain data computation is done at zero gas cost using a distributed peer-to-peer network. This entails each node retrieving data from one or more data sources, signing it with their unique private key, and broadcasting it off-chain to the rest of the Oracle network. Once sufficient responses have been generated, a single transaction containing every node’s observation is transmitted on-chain. Smart contracts can now consume this data the same way they used to. 3
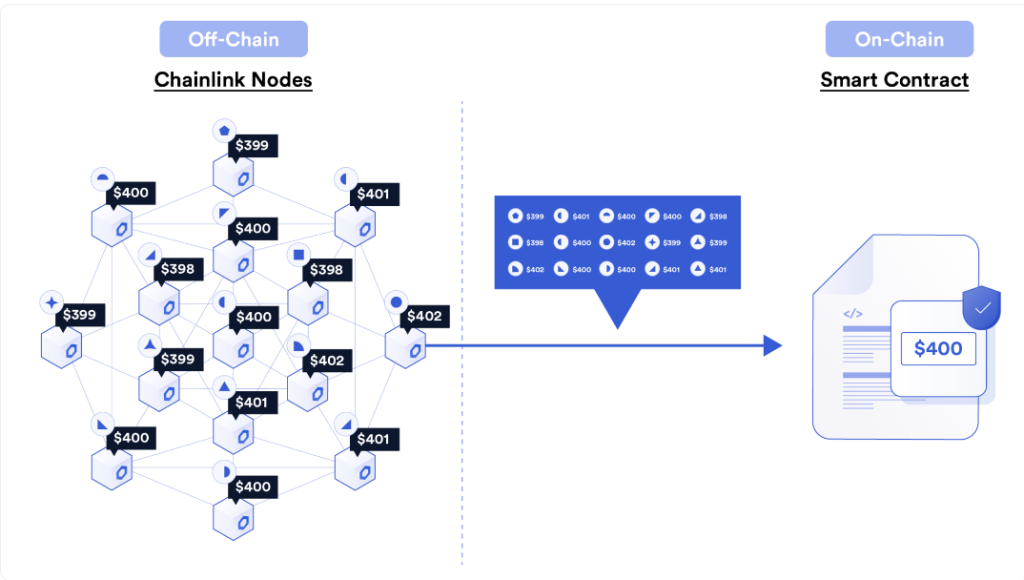
Source: https://blog.chain.link/off-chain-reporting-live-on-mainnet/
Understanding the Benefits of Chainlink Proof of Reserve for Crypto Exchanges
Proof of Reserve is a concept in the cryptocurrency industry that refers to a method of proving that an entity, such as an exchange or other custodian, actually holds the funds it claims to hold. It verifies that the entity has the reserves to back up the assets it claims to have custody of. Proof of Reserve is essential in order to build trust and confidence in custodians and exchanges, especially now, in a post-FTX-collapse era.
Chainlink Proof of Reserve provides the data required by smart contracts to calculate the true collateralization of any on-chain asset backed by off-chain or cross-chain reserves. Chainlink Proof of Reserve, powered by a decentralized network of oracles, enables real-time autonomous auditing of collateral, ensuring user funds are protected from unforeseen fractional reserve practices and other fraudulent activities. 4
Chainlink proof of reserve is also used by stablecoin projects such as TUSD, PoundToken and Cache Gold to enhance security by providing cryptographic proof that new tokens are sufficiently backed up by reserves.
Chainlink Proof of Reserve can help improve the cryptocurrency industry’s overall reputation. By demonstrating that they are improving transparency and accountability, exchanges can help counteract the negative reputation that cryptocurrency has received in the wake of collapses such as FTX.
Challenges faced by Chainlink
While it has quickly become a leader in the oracle space, there are several challenges that it and other oracle networks must address in order to continue to grow and succeed.
One challenge faced by it is the issue of scalability. As more and more blockchain-based applications are built on top of it, the demand for its services increases. However, this increased demand can put a strain on the network, potentially leading to slower response times and higher fees. To address this, it is exploring various scalability solutions, including sharding and layer-2 technologies.
Another challenge is ensuring the security and reliability of the Oracle network. As with any decentralized system, there is always the risk of attacks or hacks, which could compromise the integrity of the network and put user funds at risk. it has implemented a number of security measures to address this, including its decentralized node network and multiple layers of security and redundancy.
Finally, it must navigate the ever-changing regulatory landscape as it expands into new markets and jurisdictions. Ensuring compliance with local laws and regulations will be critical for the network’s long-term success and adoption.
While it faces several challenges, it has already made significant progress in addressing these issues and building a secure and reliable Oracle network. As blockchain-based applications continue to grow and evolve, it and other oracle networks will play a critical role in connecting these applications to the real world, unlocking new use cases and possibilities. It has become a mainstay in most blockchains and is often called the “God Protocol” which is a true testament to its functionality.
- blog.chain.link: https://blog.chain.link/chainlink-price-feeds-secure-defi/[↩]
- blog.chain.link: https://blog.chain.link/introducing-the-cross-chain-interoperability-protocol-ccip/[↩]
- blog.chain.link: https://blog.chainlink/off-chain-reporting-live-on-mainnet/[↩]
- chain.link: https://chain.link/education-hub/proof-of-reserves[↩]


