Wireless networks have become an essential part of our daily lives. With the daily increasing demand and usage of IoT devices, there is a requirement for a reliable and secure wireless network that can support these devices. That is where Helium comes into play. In this article, we will explore the Helium Future Wireless Network, its features, and its potential impact on the future of wireless networks.
What is Helium?
The Helium Network is a decentralized wireless network that utilizes a peer-to-peer architecture to provide coverage for smart devices. The helium network consists of many hotspots around the globe. These hotspots transmit a signal called LoRa which helium calls LongFi. These types of signal send a very small amount of data over a much larger range where its signals can reach up to 15km. Currently, there are more than ten thousand helium hotspots around the world and the number is increasing rapidly. All these hotspots allow IoT devices to send data over the internet at cheap rates using very low power. 1
How it works
Helium is basically a wireless network which accommodates IoT devices to hit international reach. In order to check that helium hotspots are online and transmitting signals, the helium network uses a mechanism called Proof of Coverage (PoC). The validators of the Helium blockchain randomly select hotspots to test. Once a hotspot is chosen the validator sends challenge packets to the relevant hotspot and challenges it to show that it is online by providing internet and that it is located properly. In this scenario the hotspot is called a “challenge,” and the validator is called a “challenger”. The hotspot which was chosen by a validator then transfers the above-mentioned challenge packets to other neighboring hotspots. Such neighboring hotspots are known as “witnesses”. These witnesses who received the challenge packets should send a signal to the validator by confirming that they have witnessed the challenge packet and they are online by providing internet.
After that, the validator stores all the received information in the form of a Proof of Coverage receipt transaction. Then this transaction is added to a block in the Helium blockchain and all participants including the validator, hotspot and witnesses will receive HNT tokens as a reward for their participation. Hotspots are usually rewarded for transmitting data for IoT devices and their participation in PoC challenges. When there are more witnesses that see the transmitted challenge packets, the hotspots will receive a higher reward. However, when there are more and more witnesses in the same area the witnesses will receive a lower reward. 2
Blockchain of Helium network
The helium blockchain stores all past activity of the helium network since its launch.
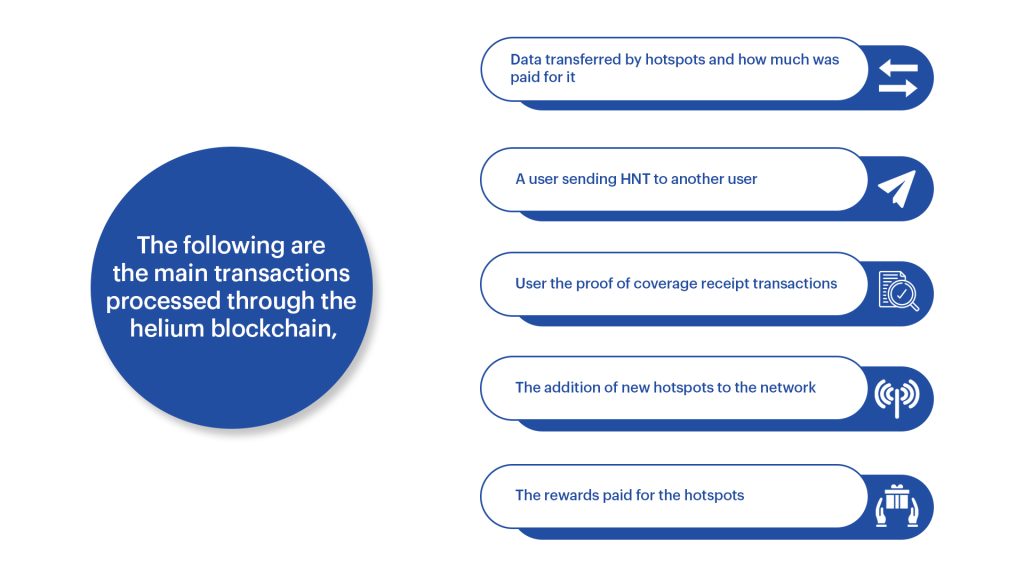
The validators on the helium networks verify these transactions and will create a block, and then add it to the blockchain. These validators are mostly cloud servers running on AWS or Google Cloud or regular computers which are connected to the network.
Helium network validator guide
To become a validator on the Helium network, it is required to stake ten thousand HNT tokens. When the validator is set up correctly, it earns around 5% APY. However, as more validators join the network, this percentage decreases. Helium employs a variation of Proof of Stake called the Honey Badger Byzantine Fault Tolerant. Validators have to lock up some tokens as collateral for any misbehavior. When a new transaction arrives it gets encrypted and the validators of the consensus group must work together to decrypt and verify these transactions before adding them to a new block in the blockchain. During the creation of new blocks in Helium, any misbehaving validators receive penalties. After an epoch has passed, which is around 30 blocks, 25% of the consensus group validators will be removed. Validators with the highest penalty scores will have the highest chance of getting removed. New validators are then selected to replace the removed ones. Validators with the lowest penalty scores in previous epochs have the highest chance of being chosen. After the new validators are selected, the consensus group begins its work of creating blocks again. 3
Advantages of Helium
- Decentralized Network: One of the most important advantages of the Helium Network is that it is decentralized. Unlike regular wireless networks that depend on centralized internet service providers (ISPs) for connectivity, the Helium Network uses a peer-to-peer network. This makes the network more reliable and secure.
- Low-Cost Deployment: Deploying a hotspot on the Helium Network is relatively easy and cheaper. The requirements are simple, all that is required is a device that can provide low-power network coverage for IoT devices. This fact makes it easier for individuals and businesses to participate in the network without the need for expensive equipment or infrastructure.
- Low-Power Consumption: Another advantage of the Helium Network is that it is designed to consume less power which means that IoT devices can operate for years with a single battery, making them ideal for applications such as smart cities, agriculture, and industrial automation.
- Earn Cryptocurrency: By deploying hotspots and verifying network transactions, users can earn a cryptocurrency called HNT. This incentivizes participation in the network by making it more reliable.
- Wide-Area Coverage: The Helium Network utilizes a distributed network of nodes or hotspots to provide wide-area coverage. This means that the network can cover large areas, making it ideal for applications such as smart cities, logistics, and transportation.
- Secure Network: The Helium Network is highly secure due to the usage of the Helium blockchain. The blockchain ensures that all transactions are transparent, making it impossible for any individual or organization to manipulate the network.
Helium Applications
The Helium Network has a wide range of applications in various industries, from agriculture and transportation to healthcare and smart cities. It provides low-cost, reliable connectivity for connected devices, enabling real-time data collection and analysis.
- Agriculture: One of the most positive applications of the Helium Network is in agriculture. Farmers can use connected devices to monitor their fields remotely and it reduces the need for manual labor and also increases efficiency. The network can be used to monitor soil moisture, temperature, and other environmental factors. The Helium Network can also be used to track the location of livestock and monitor their health.
- Healthcare: The Helium Network has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by providing low-cost reliable connectivity for medical devices. These devices can be used to monitor patients remotely and also the network can be used to track the location and condition of medical equipment reducing the risk of loss.
- Smart Cities: The Helium Network can be used to create smart cities that are more efficient and sustainable. Connected devices to the helium network can be used to monitor air quality, traffic, and energy usage, providing real-time data that can be used to optimize city operations. The network can also be used to improve public safety by providing real-time data on crime and emergency incidents.
- Industrial IoT: The Helium Network can be used in various industrial applications, including manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain management. Connected devices to the network can be used to monitor the performance of equipment, track inventory and optimize the production processes. Also, the network can be used to improve worker safety by providing real-time data on hazardous conditions and accidents.
- Retail: The Helium Network can be used in retail applications including inventory management, asset tracking and customer engagement. Connected devices can be used to monitor inventory levels, track the location and condition of merchandise and provide real-time data on customer behavior and preferences. The network can also be used to improve customer engagement by providing personalized offers and recommendations based on customer data.
Conclusion
The future potential of the Helium Network is significant. As the world becomes more connected, the need for low-cost and low-power connectivity solutions will continue to grow day by day. The Helium Network provides a unique solution to this issue, while its characteristics make it an attractive option for a wide range of industries and applications.
- Mappingnetwork: https://mappingnetwork.ca/blogs/news[↩]
- Helium.com: https://www.helium.com/[↩]
- Medium.com: https://medium.com/@mtorygreen/[↩]


