- Understanding the Lightning Network and Its Significance in Bitcoin Transactions
- How Does the Lightning Network Work?
- The Benefits of Using the Lightning Network for Bitcoin Transactions
- Potential Use Cases and Applications of the Lightning Network
- The Current State of Adoption and the Factors Driving it
- The Challenges and Limitations of Implementing the Lightning Network
- Embracing the Potential of the Lightning Network for a More Efficient Bitcoin Ecosystem
The founders of Bitcoin created Lightning Network to provide an alternative payment system that would be free from central control. They aimed to enable peer-to-peer transactions, eliminate the need for intermediaries, and reduce transaction fees. Bitcoin was designed to be secure, transparent, and globally accessible, potentially challenging the existing financial system.
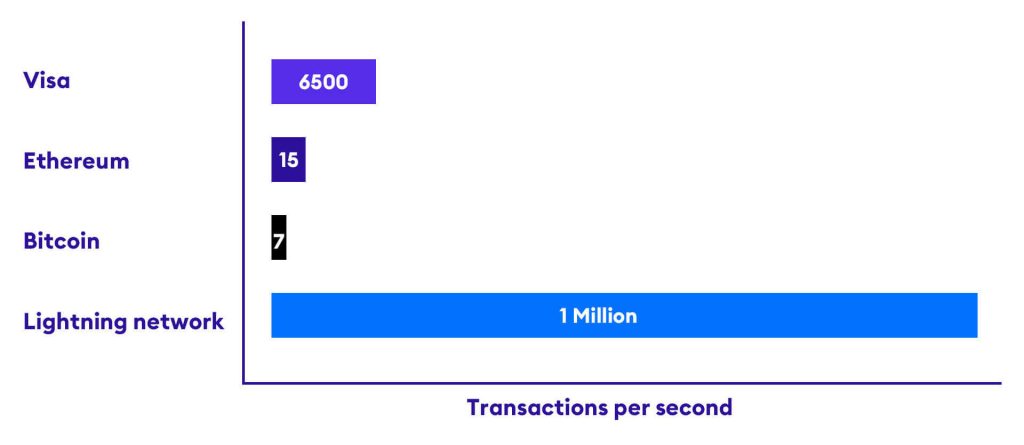
However, Bitcoin has one major drawback. Bitcoin was created with decentralization, immutability, and transparency as its core features, making the protocol a nightmare to scale. For example, Visa claims that they have the capacity to handle 65,000 transactions per second, 1 while Bitcoin can only handle 7 transactions per second 2. Yes, you read that correctly, Bitcoin only has the capacity to handle 7 transactions each second which doesn’t make it ideal to be used as an everyday payment network.
Understanding the Lightning Network and Its Significance in Bitcoin Transactions
As stated above, bitcoin was not created to act as a highly scalable and efficient payment system to handle microtransactions. For example, paying for Starbucks using Bitcoin is equivalent to using a SWIFT transaction. It is a waste of resources and not its intended purpose.
Enter the lightning network. The Lightning Network is a Layer-2 protocol built on Bitcoin’s blockchain, enabling faster and cheaper transactions. It allows users to send and receive Bitcoin instantly and with low fees, making it an attractive solution for micropayments and everyday transactions. It was proposed in 2015 by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja as a second-layer solution to enable faster, cheaper, and more scalable transactions. 3
How Does the Lightning Network Work?
To understand how the Lightning Network works, it’s helpful to first understand how Bitcoin transactions work. When you send a Bitcoin transaction, it is broadcast to all nodes on the Bitcoin network. These nodes then compete to mine the transaction, which means adding it to a block and confirming it. This process can take several minutes, and the fees can be high, especially for small transactions.
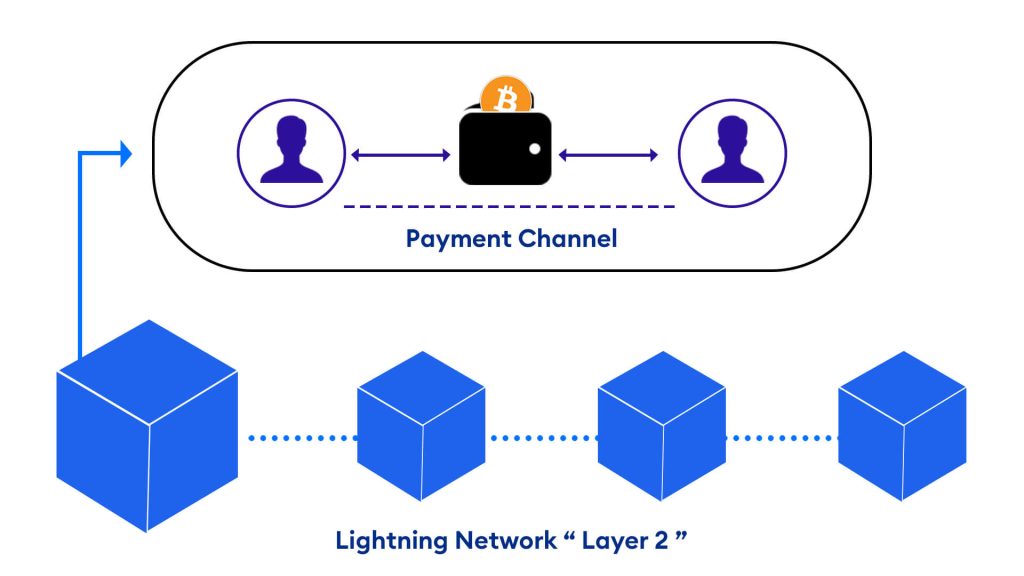
The Lightning Network works by creating payment channels between users. These channels are essentially two-party micropayment networks that allow users to send and receive Bitcoin payments without having to go through the Bitcoin blockchain.
Two users deposit Bitcoin into a multi-signature address to open a payment channel. This address is controlled by both users, so both users must agree on any transactions that take place in the channel. Once the channel is open, users can send and receive Bitcoin payments as often as they like, without waiting for confirmations on the blockchain.
When a user wants to close a payment channel, they broadcast a transaction that settles the balance of the channel. This transaction is then added to a block on the Bitcoin blockchain, and the channel is closed. 4
To sum things up, the Lightning Network enhances scalability by performing computations off-chain. It achieves this by utilizing payment channels to enable users to conduct multiple transactions without immediately recording them on the main Bitcoin blockchain. The network performs computations off-chain, reducing the burden on the blockchain and enhancing scalability. Once the participants are ready to settle their balances, the final state of the channel is recorded on the blockchain to ensure the security and immutability of the transactions.
The Benefits of Using the Lightning Network for Bitcoin Transactions
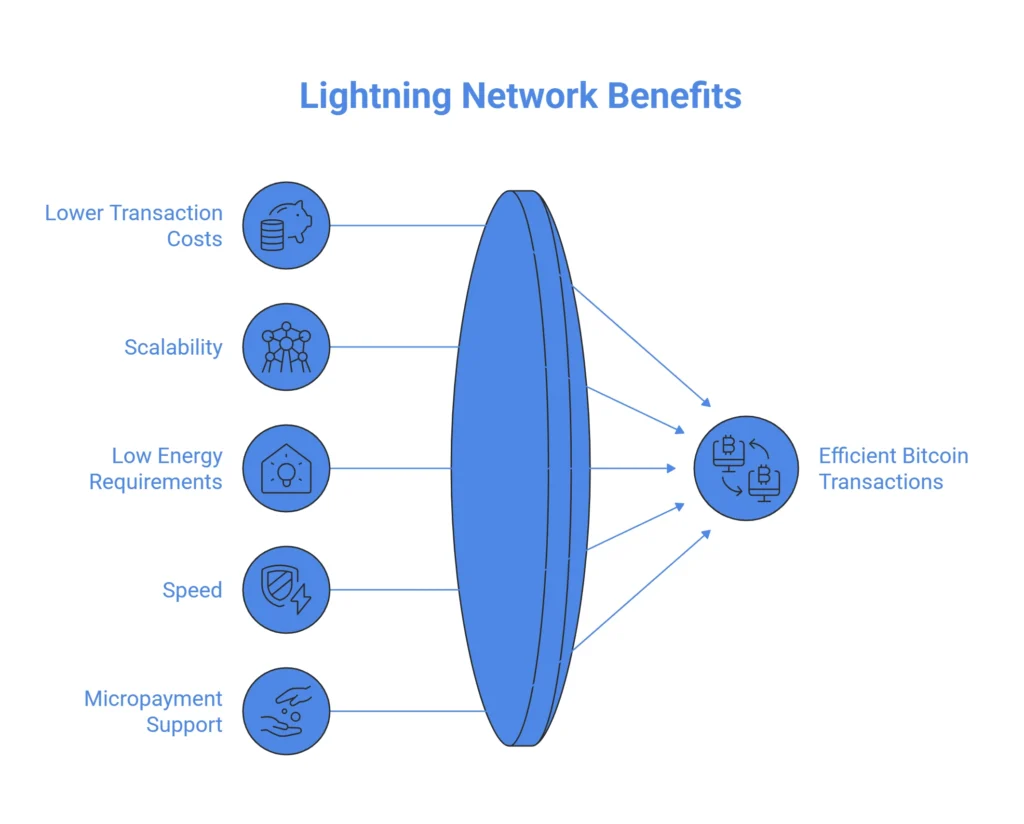
Lower transaction costs
The Lightning Network creates open channels between users for small, cheap payments and trades IOUs back and forth before settling accounts on the main Bitcoin blockchain. This means that users can save money on transaction fees, especially for small businesses.
Scalability
The Lightning Network is a technological solution intended to solve the problem of slow transaction speed on the Bitcoin blockchain by introducing off-chain transactions. It improves the scalability of Bitcoin blockchain transactions by ensuring the management of transactions external to the main blockchain network.
Low energy requirements
Considering the transactions are taken off the chain, the Lightning Network reduces the energy required to operate nodes. This has significant implications from a sustainability standpoint.
Speed
The channel allows the transacting parties to send an unlimited number of nearly instant and inexpensive transactions. It acts as its own ledger, which is core to the Lightning Network’s design.
Micropayment support
The Lightning Network provides micropayment support, which means that users can make very small transactions that would not be practical on the main Bitcoin blockchain. 5
Potential Use Cases and Applications of the Lightning Network
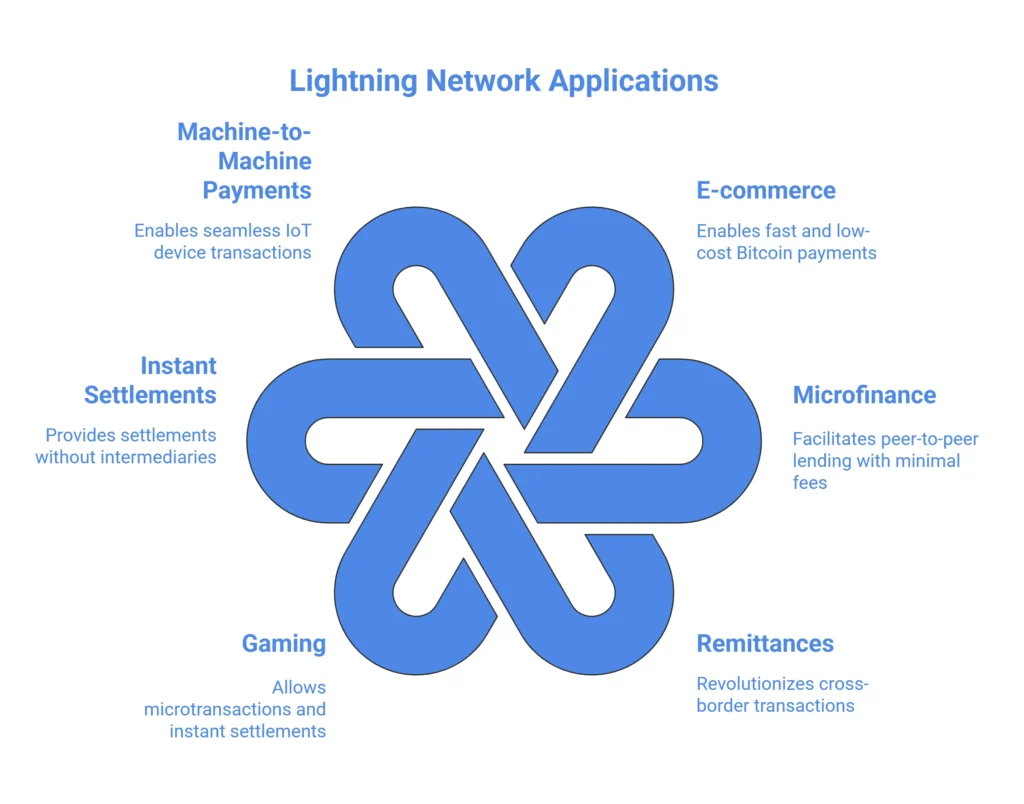
The Lightning Network has various potential use cases and applications, offering innovative solutions for fast and low-cost transactions. Here are some examples:
- E-commerce: Lightning Network can be integrated into e-commerce platforms, enabling fast and low-cost payments with Bitcoin. This reduces transaction fees and waiting times for customers.
- Microfinance: The Lightning Network can be used for microfinance applications, such as peer-to-peer lending, providing opportunities for financial inclusion and enabling small-value transactions with minimal fees.
- Remittances: The Lightning Network has the potential to revolutionize remittance services by facilitating instant and low-cost cross-border transactions.
- Gaming: Lightning Network can be applied in the gaming industry, allowing for microtransactions, in-game purchases, and instant settlements.
- Instant settlements: The Lightning Network enables instant settlements without the need for intermediaries, reducing costs for both consumers and businesses
- Machine-to-machine payments: The Lightning Network can facilitate machine-to-machine payments, enabling seamless transactions between devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
These are just a few examples of the Lightning Network’s potential use cases and applications. As adoption continues to grow, the network has the potential to disrupt various industries and communities by offering fast, low-cost, and scalable solutions for transactions. 6
The Current State of Adoption and the Factors Driving it
The network has seen significant growth in adoption in recent years. Lightning Network nodes have increased from just a few hundred in 2018 to over 16,000 as of March 2023. The total capacity of the Lightning Network has also increased significantly, from just a few BTC in 2018 to over 5,000 BTC as of March 2023. 7
There are a number of factors that have contributed to the growth of Lightning Network adoption. One factor is the increasing demand for fast and cheap payments. As the use of Bitcoin for everyday payments has grown, there has been a need for a solution that can provide these features. The Lightning Network is well-suited for this purpose, as it allows for instant payments with very low fees.
Another factor that has contributed to the growth of Lightning Network adoption is the development of user-friendly wallets and payment applications. In the past, using the Lightning Network was a complex process that required technical knowledge. However, there are now a number of wallets and payment applications that make it easy for anyone to use the Lightning Network.
The Challenges and Limitations of Implementing the Lightning Network
Channel Management
One major failing of the Lightning Network is that you must be online to pay anyone or get paid. If one party goes offline, the other party cannot close the channel, which can lead to funds being locked up. Further, each Lightning Network channel has a limited capacity, and participants need to maintain an appropriate balance of funds to enable bidirectional transactions. 8
Network Centralization
The Lightning Network relies on a network of payment channels to facilitate transactions. This can lead to some centralization, as channels tend to be established between nodes with higher connectivity and reliability. As a result, there is a risk of power concentration in the hands of a few major participants, which could undermine the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies. 8
Interoperability
The Lightning Network is primarily designed for Bitcoin, but there have been efforts to enable interoperability with other cryptocurrencies. However, achieving seamless interoperability across different blockchain networks can be technically complex and require coordination among various communities and development teams.
Regulatory Considerations
As the Lightning Network enables fast and low-cost transactions, it may raise regulatory concerns, particularly with regard to anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. In some jurisdictions, the Lightning Network’s potential for facilitating off-chain and pseudo-anonymous transactions could pose challenges for compliance with financial regulations.
Embracing the Potential of the Lightning Network for a More Efficient Bitcoin Ecosystem
The Lightning Network has grown steadily through adoption and real-world use cases. Companies like Binance are embracing the Lightning Network for deposits and withdrawals 9, offering potential solutions to scalability challenges. As the Lightning Network continues to gain momentum and more companies integrate the technology into their platforms, we can expect to see even more growth and innovation in the cryptocurrency world.
The Lightning Network has the potential to transform the way we transact with Bitcoin and other digital assets, and it is exciting to see how companies are embracing its potential. Despite adding a key dimension to enhance Bitcoin Network’s capabilities across the blockchain trilemma, the Lightning Network is not without its downsides. However, the Lightning Network is still evolving and can potentially make Bitcoin a more practical and useful currency for everyday use.
- Visa: https://visa.co.uk[↩]
- Crypto.com: https://www.crypto.com[↩]
- arxiv.org: https://www.arxiv.org[↩]
- Decrypt: https:www.decrypt.com[↩]
- Cointelegraph: https:www.cointelegraph.com[↩]
- Cryptoglobe: https://www.cryptoglobe.com[↩]
- lookintobitcoin: https://www.lookintobitcoin.com[↩]
- Makeuseof:https://www.makeuseof.com/risks-issues-bitcoin-lightning-network/ [↩][↩]
- Binance: www.binance.com[↩]


