- The 4 Main Types of Blockchain Networks
- Understanding Permissioned & Private Blockchains for Business Solutions
- Exploring the Benefits of Consortium Blockchains for Collaborative Solutions
- Using Sidechain Technology to Unlock Advanced Blockchain Features
- Conclusion: Understanding the Different Types of Blockchains to Choose the Right One for Your Needs
Unless you have been living under a rock for the past few years, bitcoin should not be an unfamiliar term. Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that enables secure peer-to-peer payments without a centralized authority. This feat is achieved through Blockchain Technology.
Blockchain is a digital ledger technology that uses cryptography to store transactions securely. It stores data in groups known as blocks. Each block contains the relevant transactions and a timestamp and is cryptographically linked to the previous block, making it resilient to tampering. The chain is maintained by a network of users, called nodes, who work together to validate new transactions and add them to the blockchain.
Bitcoin is the first and most widely used application of blockchain technology. However, blockchain technology can be applied to other use cases, such as supply chains, voting systems, identity management, etc.
In this article, we will be exploring the different types of blockchains and their respective use cases.
The 4 Main Types of Blockchain Networks
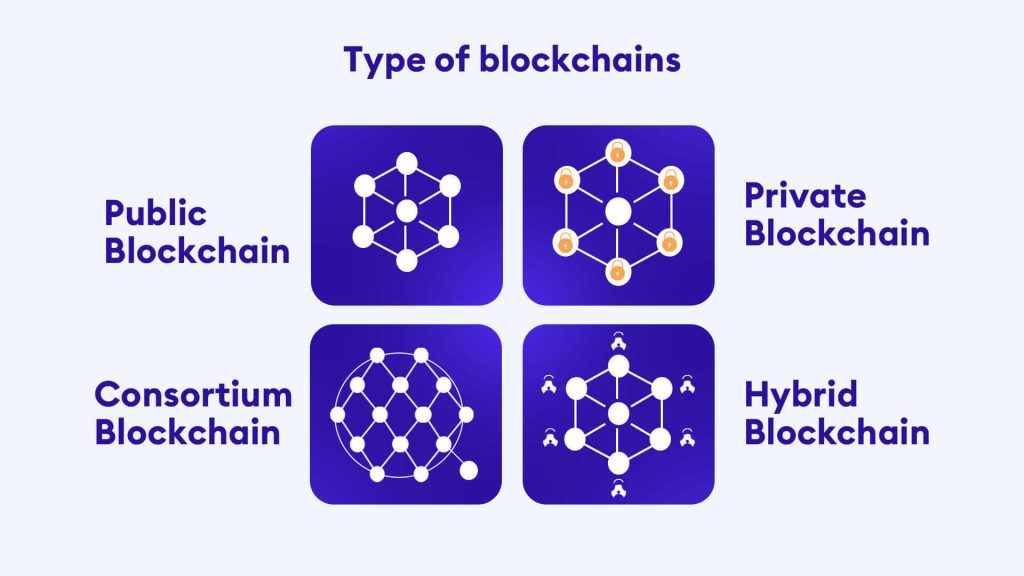
As the name implies, public blockchains are open, and anyone with an internet connection can join and participate in the core activities of the network. Moreover, all network participants can access current and past data, making auditing convenient. Their open and transparent nature makes it the ideal infrastructure to promote self-governance and decentralization.
Public blockchains are the first type of available blockchains and can be seen in cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. They also serve as the backbone on which most DeFi systems are built. Since public blockchains are non-restrictive and permissionless, so many network participants are attracted. This allows for greater security but can also make the network slow.
Private Blockchains
Unlike their public counterparts, private blockchains are centralized networks restricted to a specific group of participants. They operate similarly to public blockchains because they use peer-to-peer connections and nodes to run the network. The difference is that these nodes have restricted access, and not all nodes can edit or view the ledger. Further, the owner of the network has the ability to override or delete data.
Organizations typically use private blockchains for internal record-keeping and other private transactions. These networks aren’t as extensive as public networks, which allow far greater speeds. In addition, the controlling entity can set permission, security, and authorization levels for individual nodes granting more control over the network. Lastly, private blockchains offer more privacy, and sensitive information can be safeguarded as they run in a closed network.
Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains are a combination of public and private blockchains, allowing for a merger of public accessibility and private control. Entities can set up a private, permissioned system alongside a public, permissionless system, allowing them to control who has access to specific data and what data is publicly accessible. Using this approach, confidential information can be verified without exposing its contents, which is achieved through smart contracts.
Hybrid blockchain offers a high level of security due to its ability to protect against 51% attacks. This is because it only allows authorized users access to the network. Since the number of nodes verifying transactions is smaller, the overall cost of running the network will also be reduced. One drawback of this approach would be the lack of incentives for network participation due to its closed nature.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains, also known as federated blockchains, are similar to hybrid blockchains due to the presence of public and private blockchain features. However, the difference is that it is not limited to one organization; multiple organizations can work together on a decentralized network. In addition, these systems can be used for various applications, such as supply chain management or voting systems.
A consortium blockchain is more secure, scalable, and efficient than a public blockchain. It, like private and hybrid blockchains, also provides access controls, but it lacks transparency compared to a public blockchain. 1
Understanding Permissioned & Private Blockchains for Business Solutions
A permission blockchain is a private blockchain that allows specific individuals or organizations to be granted access or “permission” to join the network and validate transactions. This can be useful for businesses that want to maintain network control while allowing multiple parties to participate and validate transactions.
As explained above, a private blockchain is only accessible to a specific group or entity and is used for internal operations and record-keeping. It can be used to increase security and efficiency for particular business processes and can also be customized to fit the organization’s specific needs.
Both permissioned and private blockchains can be used for various business solutions, including supply chain management, digital identity verification, and recording financial transactions. They can also be integrated with existing systems and used in conjunction with public blockchains for additional functionality. 2
Exploring the Benefits of Consortium Blockchains for Collaborative Solutions
As stated above, consortium blockchains are mainly geared toward multi-organizational systems. Essentially, these are private blockchains with users in multiple organizations.
Consortium blockchains have proven to be highly effective in research, where multiple research organizations can collaborate by sharing and validating data. Other industries where these can be used include finance and banking, where numerous financial institutions can work together using a distributed ledger to increase efficiency and reduce cost. It is also ideal for use in time-sensitive supply chains associated with food and medical products.
Using Sidechain Technology to Unlock Advanced Blockchain Features
A sidechain is a separate blockchain linked to the main blockchain, allowing assets and information to be transferred between the two chains. Sidechain technology unlocks advanced features such as scalability, interoperability, and privacy.
The main advantage of sidechains is that they allow for greater flexibility and scalability compared to a single blockchain. For example, a sidechain can offload some of the transactions from the main blockchain, allowing it to process more transactions per second.
Sidechains can also be used to transfer assets and information between different blockchain platforms, enabling them to communicate and interact with each other. This allows for cross-chain transactions and decentralized applications that span multiple blockchain networks.
Additionally, sidechains can be used to increase privacy, as sensitive information can be kept on a private sidechain while still being able to interact with the public blockchain. This allows for use cases such as confidential transactions and smart private contracts. 3
Conclusion: Understanding the Different Types of Blockchains to Choose the Right One for Your Needs
The world of blockchain technology constantly evolves and offers a wide range of options to suit diverse needs and applications. Therefore, it is essential to carefully evaluate your specific requirements and consider the trade-offs between security, scalability, and decentralization. It is also crucial to consider the regulatory environment and the ecosystem in which your blockchain will operate. By understanding the different types of blockchains available, organizations can make an informed decision on the best option for their project and leverage the power of this innovative technology to drive their business forward.
- geeksforgeeks.org: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/types-of-blockchain/[↩]
- Investopedia.com: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/permissioned-blockchains.asp[↩]
- 101blockchains.com: https://101blockchains.com/sidechains-blockchain/[↩]