What is Digital Money?
Money has been used for centuries as a medium of exchange and a store of value. Each government has a central bank that has the power to influence the value of the local currency. The local currency value is measured against the reserved foreign currency, such as the US dollar, and this relationship determines the exchange rate of the local currency. When this traditional fiat currency takes a digital form, we call it a digital currency. But, of course, electronic versions of fiat currency are also available, so don’t confuse them with their digital counterparts. For ease, let’s assume that you have a bank account and you’re going to an ATM to withdraw it; this clearly shows that electronic currency can be converted to physical currency. This is the main difference between electronic currency and digital currency. Electronic currency is any currency available in electronic form, which you can transform into its physical form. Digital currency (CBDC), however, never takes physical form and always runs through computer systems and networks.
Why is Digital Currency Important?
- Reasons to Create a Digital Currency With the recent significant adoption of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, even Governments have started to witness the benefits of digital currencies. They are a great practical alternative to traditional fiat currencies. However, Fiat currencies contain many drawbacks with them. Starting from long transaction times, cumbersome procedures to make an overseas transaction, Physical manufacturing, and inability to perform instant transactions. With the help of advanced frameworks and technologies, digital currencies will solve most of the problems we face with traditional fiat currencies. Starting from Safekeeping since they do not require physical storage, Security, Easy tracking opportunities for government bodies, Autonomy, Fast transactions, Minimal fees, and relatively high trust between merchants and customers.
- First Digital Currency According to Wikipedia, the concept of digital currency was initially suggested in “Blind Signatures for Untraceable Payments,” a research paper by David Chaum. Later several assets came to market, like e-gold, Bitcoin, and QQ coins1.
- Future outlook Following the successful launch of Bitcoin, the demand for decentralization is growing. In November 2021, the market capitalization of digital assets reached $3 trillion 2.
What is a CBDC
Central bank digital currencies, commonly known as CBDC, are government-issued digital currencies, inherently not volatile, unlike other crypto assets, backed by the country’s fiat currency. In simple terms, CBDC is the digital form of a country’s fiat currency. As we mentioned earlier, it will not take any physical form as electronic money does. Instead, it will only run through computer systems and networks. They are intended to function as a means of payment, like physical cash or bank deposits, but in a digital form. One key difference between CBDCs and traditional fiat currencies is that CBDCs can be issued and tracked digitally, potentially allowing central banks more control over the money supply and better monitoring of financial transactions. Some of you may think that this is a novel concept. But it has been around for a few decades. According to the IMF, A dropped project called Avant Smart Card, a CBDC of the Bank of Finland which dates to 1993 is believed to be the world’s first CBDC. Central banks all over the world are now exploring their potential benefits, including how they improve the efficiency and security of payment systems.
Why Governments are Creating CBDCs
According to the IMF (International Monetary Fund), nearly 100 CBDC research and development projects were going on as of July 20223. Of course, countries have different motives and agendas behind this. But exclusively, they can create greater resilience for domestic payment solutions.
When we look at the history of reserve currencies, the Spanish silver dollar is considered the world’s first global reserve currency. The Bretton Woods Agreement established the United States dollar as the world’s primary reserve currency in 1944. It claimed this status from sterling after the devastation of two world wars and the massive spending of the United Kingdom’s gold reserves. Almost 8 decades later, countries are still settling international balances and doing international invoicing in US Dollars. By any measure, the US dollar is still the dominant global currency for funding markets.
Advantages
By having a CBDC, governments can deliver most of the advantages of a digital currency coupled with the credibility of fiat currency in one package. Starting from easy tracking opportunities and transparency in money flows. This may sound absurd. But when we examine things closely, we can get an idea of its benefits. For example, the US Dollar has been a prominent global reserve currency for many years. Even though the US Government has yet to learn precisely how much of their reserves are flowing overseas. By creating a framework, we can easily monitor them, like how we are getting on-chain data for cryptocurrency.
The next potential benefit is financial inclusion. CBDCs can make it easier for the unbanked or underserved by traditional financial institutions to access and use financial services. This is because CBDCs can be accessed and used through various digital platforms, including mobile phones and other devices, making it easier for people to conduct transactions and manage their finances even if they don’t have a bank account. In addition, the penetration of mobile phones in remote areas is higher than the banking system’s availability. CBDCs can be transferred and settled instantly, making transactions faster and more efficient. This can be particularly beneficial for cross-border payments, which can be a relatively slow process that takes 2-3 days to process and is costly using traditional financial systems.
Since they can track the supply of the CBDC, they can reverse-track fraud or criminal activity. When fraud happens with traditional fiat money, it is a time-consuming and effort-taking process for law-and-order entities. With CBDCs, we can potentially reduce those efforts. Since they are backed by a central bank, CBDCs can offer more stability in effectively maintaining their value than any other asset-backed currencies, such as stablecoins.
CBDCs can reduce the costs associated with financial transactions, as they can be settled directly between the parties involved without the need for intermediaries like banks or payment processors. Traditional currency always requires a safekeeping mechanism to reduce the risks of being stolen since they are physical. But CBDCs can do them effortlessly since they are equipped with security features like encryption and digital signatures to protect against fraud and counterfeiting.
CBDCs can provide central banks with additional tools to implement enhanced monetary policy, such as conducting hostile interest rate policy or managing liquidity more effectively in the financial system. Finally, they can offer greater transparency in the financial system. They can be tracked and recorded in real-time, giving central banks and other authorities better visibility into economic activity and helping to prevent financial crimes like money laundering and terrorist financing.
Disadvantages
Despite these advantages, some potential challenges and risks are associated with adopting CBDCs.
Since this is a very technical subject, older generations and non-tech-savvy people may need help to adopt it. Moreover, this will result in operational difficulties. Therefore, governments must work on adopting mechanisms and creating bridges to facilitate the transition. Some people may be concerned about the potential for CBDCs to be used to track and monitor their financial activities, which could impact their privacy.
As with any digital technology, CBDCs are also vulnerable to cyber-attacks and other forms of digital fraud, which could pose a risk to the financial system’s stability.
The adoption of CBDCs could also contain an additional pressure that they potentially disintermediate traditional financial institutions, such as banks, which could impact their business models and profitability. This may require significant changes to existing legal and regulatory frameworks, which could be complex and time-consuming.
Stable Coins
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency pegged to the value of a specific asset, such as a fiat currency or commodity. The goal of stablecoins is to provide the benefits of cryptocurrency, such as fast and cheap transactions and increased financial accessibility while eliminating the volatility inherent in many cryptocurrencies. Furthermore, because stablecoins are pegged to the value of a specific asset, their importance should remain relatively stable, making them more suitable for use as a medium of exchange or store of value. Sounds similar to a CBDC. But they have fundamental differences, which we will explore below.
Differences between Stable Coin and CBDC
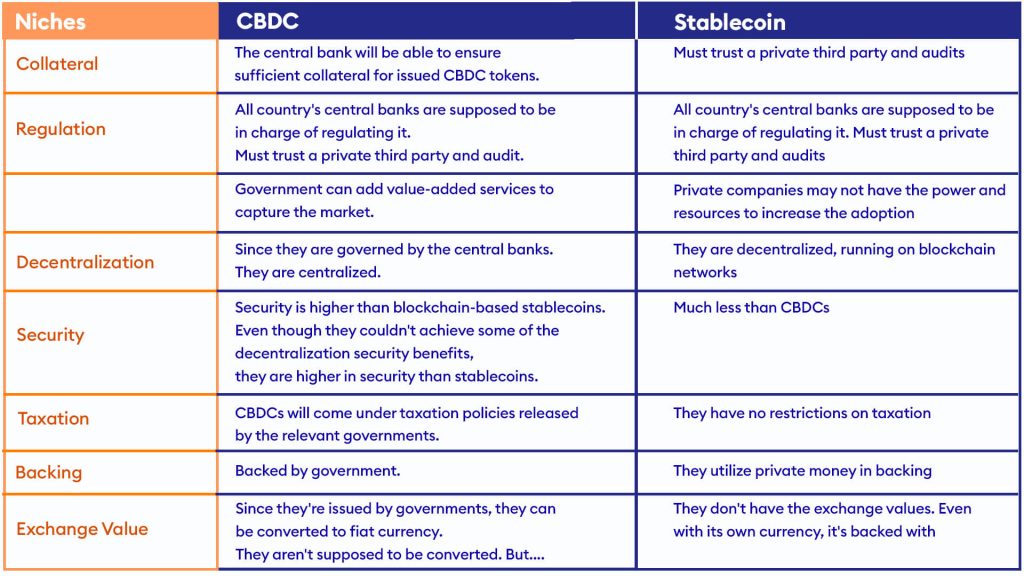
CBDCs and stable coins are both digital currencies that have the potential to improve the efficiency and accessibility of financial transactions. Still, they differ regarding who issues them and how they are backed. For example, CBDCs are issued and backed by central banks, while stablecoins can be issued by various entities and are typically backed by a specific asset or basket of assets.
The central bank will act as the central regulatory authority for a CBDC, while there is no such entity for a Stablecoin. Regarding Decentralization, CBDCs are more centralized than stablecoins, as they are governed by central banks. Although stablecoins are more decentralized than CBDCs, CBDCs lose the security benefits associated with them. Still, they are much more secure than stable coins as there is no risk of de-pegging, which is one of the main concerns related to stablecoins. In some countries, stablecoins can be considered cryptocurrencies, but this will be a disadvantage in taxation.
Can the US Government Create a CBDC?
The US government is considering the benefits of creating a central bank digital currency, or CBDC. They have been researching it for quite some time, and many believe that it will be a good idea to implement one in the future.
We can’t say whether or not this will happen, but there are a lot of benefits to the US Government creating a CBDC for the American people. It would allow them to use cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin as legal tender in transactions with the government and other banks, which would mean more liquidity and lower transaction costs for everyone involved in these transactions. This would also reduce fraud because all transactions would be recorded on an immutable blockchain ledger that is accessible by all parties involved with no chance of alteration or deletion – something that is impossible with traditional fiat currencies today.4
Conclusion
“The ongoing debate over the risks and benefits of a CBDC is important, and I am happy to continue to engage with both advocates and skeptics of CBDCs. But, for the reasons I have laid out, I don’t think there are implications here for the role of the United States in the global economy and financial system. We should instead focus on and debate the salient CBDC-related topics, like its effects on financial stability, payment system improvements, and financial inclusion. Thank you again for having me participate in this fantastic event.” a speech was given at the symposium “Digital Currencies and National Security Tradeoffs”, presented by the Harvard National Security Journal, Cambridge, Massachusetts by Christopher J Waller5.
CBDCs offer several potential advantages over traditional fiat currencies, including increased financial inclusion, improved efficiency and speed, reduced transaction costs, increased stability, and enhanced monetary policy tools. However, some potential challenges and risks are associated with adopting CBDCs, including privacy concerns, cybersecurity risks, disintermediation of traditional financial institutions, and regulatory challenges.
This paper will conclude that Central Banks should invest in creating a Central Bank Digital Currency, or CBDC. The benefits of a CBDC are far-reaching, and the risks are manageable. There is no reason for Central Banks to not invest in this technology and there is much to gain from doing so.
- Digital Currency – Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_currency[↩]
- ECB: https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/key/date/2022/html/ecb.sp220425~6436006db0.en.html[↩]
- The Future of Money: Gearing up for Central Bank Digital Currency IMF.org : https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2022/02/09/sp020922-the-future-of-money-gearing-up-for-central-bank-digital-currency[↩]
- CBDC – FAQ, from Federal Reserve: Federal Reserve Board – FAQs[↩]
- Federal Reserve Board: Speech by Governor Waller on the U.S. dollar and central bank digital currencies – Federal Reserve Board[↩]