Table of Content
What exactly is a Blockchain Bridge?
Blockchain, by nature, is closed off and exists as an isolated ecosystem. This is a major bane for the development of the blockchain industry as a whole, as it prevents the pooling of resources and achieving synergy. Imagine a blockchain bridge as a virtual connection that allows different blockchain networks to communicate and share information with each other. This concept can be compared to a wormhole in space, which acts as a tunnel connecting two distant points, allowing objects to travel between them instantaneously.
In the current blockchain landscape, various networks exist, each with its own set of consensus mechanisms and protocols. These networks are like distant planets in space, and they cannot directly interact with one another. A blockchain bridge serves as a portal, just like a wormhole, connecting these isolated planets (blockchain networks) so they can exchange data and assets seamlessly.
What is the purpose of Blockchain Bridges?
As Web 3 evolved and became more established, a notable challenge in the blockchain sector was the requirement for different blockchains to work together. Each blockchain had its own rules, cryptocurrencies, protocols, and smart contracts. To address this issue, blockchain bridges were introduced to dismantle these isolated systems and link the decentralized crypto ecosystems.
How do Blockchain Bridges Function?
Blockchain bridges operate by using a process called “wrapping” to facilitate the exchange of tokens across different blockchain networks. When a user wants to move a token from one blockchain to another, they initiate a wrapping transaction on the original blockchain.
During this process, the token is locked or “wrapped” on the original chain, and an equivalent token is created on the destination chain, representing the same value. This wrapped token can then be freely traded and utilized within the destination blockchain ecosystem. To return the token to its original blockchain, it undergoes a similar unwrapping process, where the wrapped token on the destination chain is destroyed, and the original token is released on its native blockchain.
This wrapping and unwrapping mechanism ensures the seamless transfer of tokens between different blockchains and is a better alternative to buying and selling on different blockchains, which pose transaction and volatility risks.
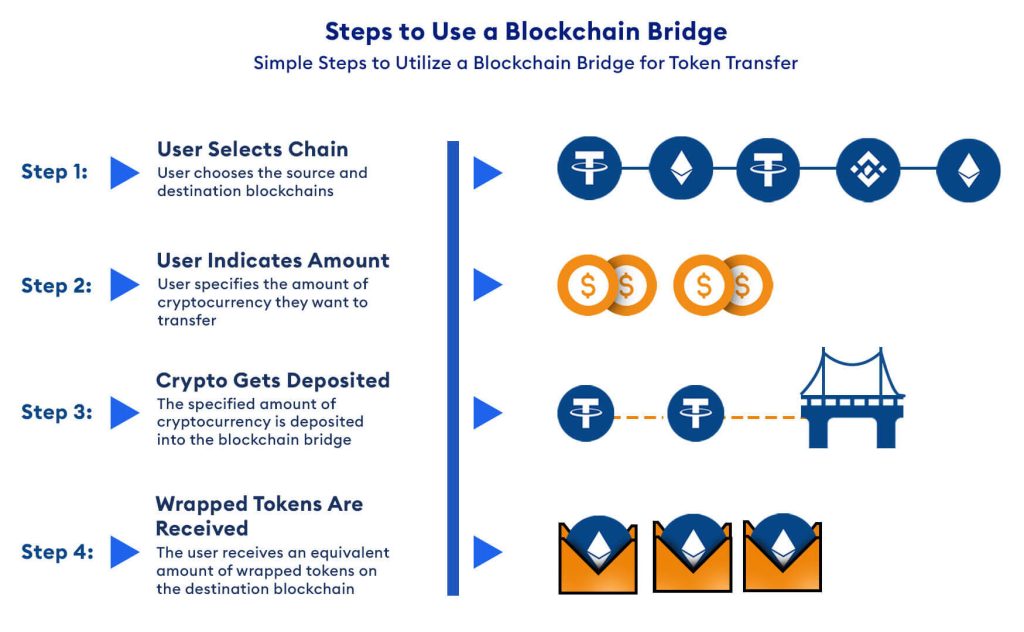
This method involves a few phases from the standpoint of the user. To utilize a bridge, for example, pick the chain you want to bridge and then indicate the amount. The cryptocurrency will subsequently be deposited at an address established by the bridge.
The bridge will deliver you an equal quantity of wrapped tokens on the other blockchain when the crypto is transferred to the address within the time frame. If you wish to convert your money back, repeat the procedure. 1
Blockchain Bridge Types

Uni-directional bridges, bidirectional bridges, federated bridges, sometimes known as trustworthy bridges, sidechain bridges, and cross-chain bridges are all sorts of blockchain bridges. Each of these bridges functions as follows:
- Uni-directional and bidirectional bridges: Uni-directional bridges allow for one-way asset transfers, while bidirectional bridges allow free asset transfers between two blockchains. A wrapped Bitcoin is an example of a one-way bridge. You may use your Bitcoin to produce tokens (WBTC) with the same value as ETH. It only works the other way around. On the other hand, uni-directional bridges such as Wormhole let you transfer tokens between Solana and other top Defi protocols. 2
- Bridges That are Federated or Trusting: Federated bridges are blockchain bridges managed by a federation of trustworthy organizations or people. The federation enables asset transfers between the two networks and ensures the transfers are safe, per applicable legislation. An example of a federated bridge can be found in the Ripple Network, which employs a network of trusted validators to allow asset transfers across multiple payment networks. Banks and financial organizations utilize the Ripple Network to transmit money and other assets globally, and it is supposed to be quicker and cheaper than conventional payment systems. 3
The Drawbacks of Utilizing Blockchain Bridges

Blockchain bridges, on the other hand, have certain limits. First, attackers have taken advantage of flaws in the smart contracts of several blockchain bridges. Second, malicious actors have stolen massive sums of cryptocurrency from cross-chain bridges. Third, users may be exposed to custodial dangers while using custodial bridges. For example, a centralized body operating behind a custodial bridge can hypothetically steal money from its users. Therefore, when utilizing custodial bridges, look for well-known product companies with a proven track record. Fourth, transaction rate bottlenecks are another possible technological barrier. Finally, the throughput capacity constraint of a single chain might stymie large-scale blockchain interoperability.
Final Thoughts
Constant innovation drives the growth of the blockchain sector. The pioneer protocols, such as the Bitcoin and Ethereum networks, are followed by numerous alternative layer 1 and 2 blockchains. As a result, the number of cryptocurrencies and tokens has exploded, emphasizing the need for increased interoperability to link their various policies and technologies. A blockchain ecosystem connected by bridges is more coherent, allowing for greater scalability and efficiency. However, with several assaults on cross-chain bridges, researchers and developers are looking for a more secure and resilient bridge architecture.
- Binance: www.binance.com[↩]
- CNBC TV: www.cnbctv18.com[↩]
- Pulse on Linkedin: www.linkedin.com[↩]