Table of Content
The new economy is upon us. The digital world has forever changed the way we communicate and do business. Social media has driven companies to connect with their target audience to stay ahead of the curve with marketing campaigns and brand identity. Companies need an online presence to remain competitive in today’s market, and services such as Google Maps and Facebook have become more essential than luxury. Digital technology is also responsible for the explosion in e-commerce, which is driving much of the new economy. E-commerce transactions now exceed traditional brick-and-mortar retail spending, and companies like Amazon are starting to impact many industries significantly. Decentralization is a system of organizing things in which the power is not concentrated in one person or group. It is the opposite of centralization. Decentralization is not just a buzzword. It’s the new economy.
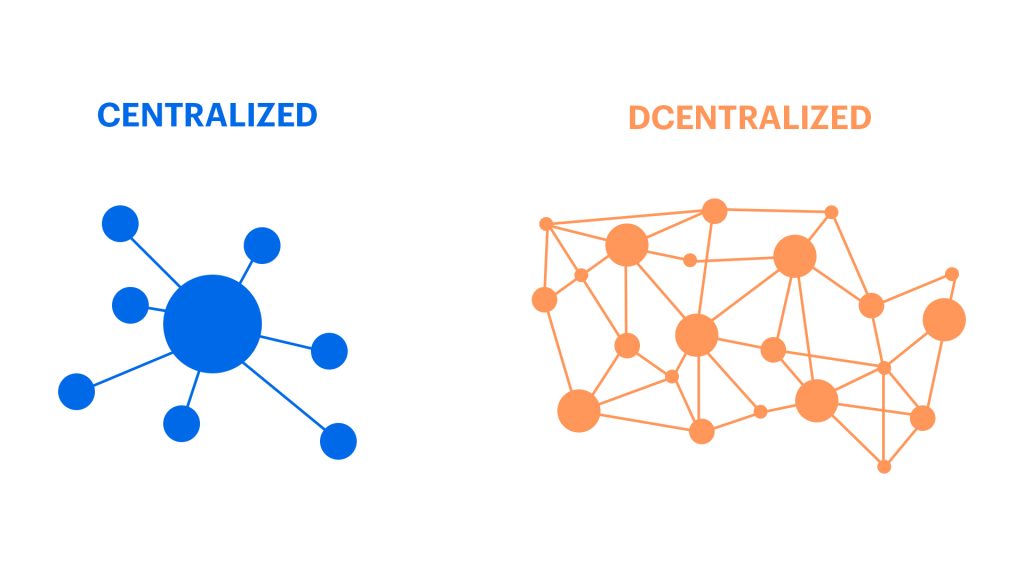
Decentralized networks exist without any central point of control. They are more democratic, as no single entity or person having more power than others and they are more secure because there is no single point of failure for an attack to target.
The internet itself evolved out of a conception of a decentralized network of computers; it does not rely on a single company or entity to function but instead on a vast network of interconnected computers that share information through a system called “the internet.” This means that if one node goes offline, the rest of the network can operate as usual. This decentralization has been made possible by blockchain technology. Blockchain is a new type of database that runs on peer-to-peer networks rather than one centralized system. As a result, blockchain databases are not controlled by any single person or organization but instead rely on distributed consensus from the network’s users. This creates an economic incentive for everyone to participate in the network, with no one person or group able to control it.
Blockchain technology has already begun to significantly impact industries like finance, manufacturing, advertising, and more. With more than $500 billion invested in blockchain since 2011, it’s clear that decentralization is here to stay.
This article will explore everything you need to know about decentralization, including what it is, its causes, examples of its impact thus far, critical risks involved, and potential benefits of decentralization.
What is decentralization? Why is decentralization necessary?
As digital technology has grown in importance, so have its inherent problems. Centralization often proves problematic, particularly in finance, healthcare, and government industries. These sectors face the challenge of increasing complexity and, as a result, increased risk. Increased complexity can lead to errors, which are expensive to correct, and poor decision-making, which can cause significant harm to the public. In these cases, decentralization can improve efficiency and cost-effectiveness by removing unnecessary layers to increase efficiency.
How does blockchain work?
Blockchain is a decentralized network that maintains a record of transactions across many computers. Its decentralized nature means no single party is responsible for recording transactions, which decreases the risk of human error and creates a more secure system. The blockchain is an immutable record of all information. It stores transactions as blocks, and each block is linked to the previous one. Other computers on that network will reject any attempt to modify data on the blockchain because it would break the link between two consecutive blocks.
This ensures that the data cannot be tampered with and that the information has not been fraudulently altered. It can be used as a system of trust between two parties when trading goods or services with one another, even if they have never met. 1
Benefits of Decentralized blockchain-enabled systems
- Reduced complexity and risk: A key benefit of decentralized networks is that they inherently reduce inherent risk. Complex systems often lead to increased risk because they lack a clearly defined control framework. Decentralized networks, however, pose a clear framework that can help to mitigate this risk.
- Improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness: More efficient systems are typically less expensive to run, which increases profit margins. Improved efficiency can also reduce the costs associated with intermediation, compliance, and governance, which can be particularly significant in complex industries.
Risks of Decentralized Blockchain Systems
- Lack of scalability: The most significant risk associated with blockchain networks is that they won’t be able to scale to handle large numbers of users. If this happens, then decentralized applications that rely on blockchain as their underlying technology may not be able to function correctly.
- Asset/token mismanagement: Asset/token mismanagement is a significant risk associated with decentralized blockchain systems. Once assets are issued on these networks, they must be appropriately managed.
- Cybersecurity threat: Another risk associated with decentralized blockchain systems is that they’re not sufficiently protected against cybersecurity threats. If a network is hacked, it is possible to steal tokens, which can have significant financial and contractual implications. 2
Conclusion
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions in a secure, decentralized, and immutable way. A blockchain is a data structure that stores blocks of information. Each block contains a timestamp and links to the previous block. Blockchains provide security by making it nearly impossible to tamper with any one block without changing all other blocks in the chain. Decentralization is the future of technology. With the rise of blockchain, it has become easier to create decentralized apps and smart contracts. The system also eliminates any single point of failure as everything is replicated and distributed among the nodes in a network. DAPPS are applications that run on a peer-to-peer network of computers rather than on a single computer or server.
It has become clear that it will be the future of many technologies, including communications, finance, and even governments. In the future, finding a company that doesn’t use blockchain will be hard. It is not just for cryptocurrencies anymore. Blockchain has the potential to change many industries and even our society.
- Wikepedia: wikipedia.org[↩]
- Sharedum: sharedom.org[↩]


