Avalanche is a heterogeneous network of blockchains that rivals Ethereum. It’s well known because of its scalable solutions, interoperability, and transaction speeds.
It can process about 4,500 transactions per second, whereas Ethereum can only process about 30 transactions per second. To achieve this, it uses a novel approach utilizing three separate blockchains under its primary chain.
The term “heterogeneous” in the context of the Avalanche blockchain refers to the platform’s ability to support multiple, distinct, and customizable blockchains or subnets within the same network. Each of these blockchains can have different rules, consensus mechanisms, and characteristics, making them heterogeneous or diverse in nature.
At its core, Avalanche uses a consensus protocol called Avalanche consensus. Unlike other consensus protocols like Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake, Avalanche consensus is a new family of protocols that relies on a randomized, leaderless, and asynchronous process to reach consensus.
This means that multiple validators can propose conflicting transactions simultaneously, and the network can reach a consensus quickly and efficiently. Avalanche also uses a unique architecture of three interrelated chains: x-Chain, p-Chain, and c-Chain. Together, these chains form a decentralized ecosystem that can support various use cases, such as cryptocurrency payments, asset tokenization, and smart contracts. In this article, we’ll look at what they are and how they operate.
Introduction to Avalanche Chain
Let’s use an analogy of a large company with multiple departments and employees to better understand how these chains work.
The x-chain is like the company’s finance department, responsible for managing the company’s funds. P-chain is like the Human Resources department of the company, where managing the company’s personnel and their resources takes place. And finally, the c-chain is the project management department. It will work on delivering the results of the projects.
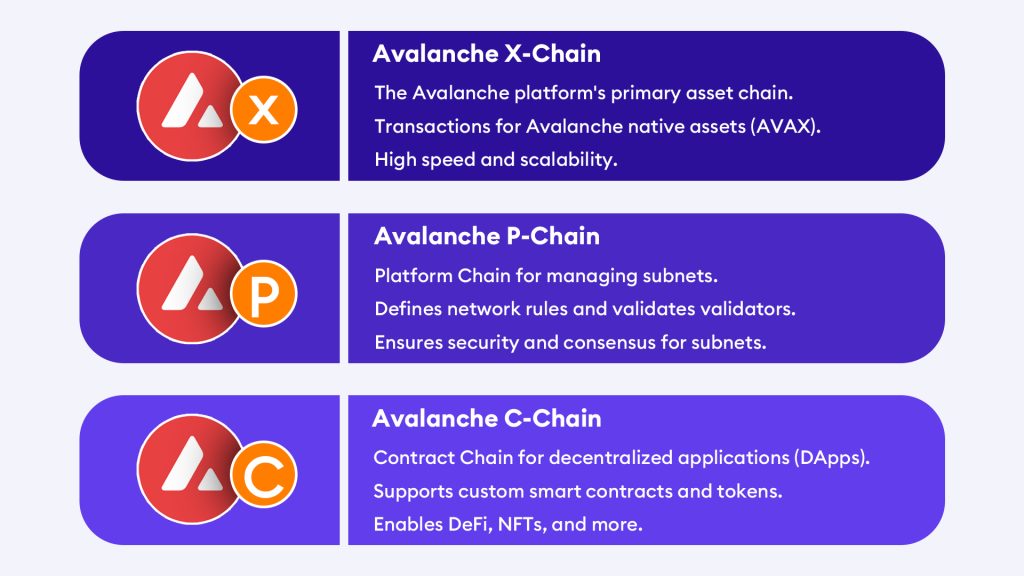
Similarly, Avalanche’s x-Chain handles transactions, the p-Chain manages the validators and governance, and the c-Chain is responsible for creating and issuing new digital assets on the network.
Together, they create a decentralized ecosystem that offers scalability, security, and flexibility for various use cases.
What are the differences between the chains, and how do they work?
- C chain
- The C stands for Contract; hence, developers use this chain to create smart contracts for DApps. C chain addresses begin with 0x, the same as Ethereum since Avalanche implements an instance of the Ethereum Virtual Machine and enables DApp EVM compatibility. Snowman is a modified version of the Avalanche Consensus Protocol and is the protocol that facilitates both the C-chain and the P-chain.
- P chain
- The P chain stands for Platform, and it coordinates with network validators. It allows you to stake AVAX and serve as a validator for the network. If you are a validator or delegating to a validator, then your AVAX rewards will be received on this chain. Chain addresses begin with “P-Avax.”1
- X chain
- X chain or Exchange chain is always used to send and receive funds. Transaction fees will be paid in AVAX, and this chain uses the Avalanche Consensus protocol (explained below). What are subnets? Subnets are smaller networks within a larger network. They are created by subnetting, which divides a larger network into smaller, more manageable parts. Subnets improve network performance, security, and manageability by limiting the size of network segments, establishing separate security zones, and assigning each subnet a unique network address.
What is the Avalanche Consensus Protocol?
The Avalanche consensus protocol follows proof-of-stake closely but has some modifications. Unlike the usual proof-of-stake or even PoW concepts, it doesn’t matter how many nodes there are to reach a consensus within a certain timeframe. They are using a form of subsampled voting, where participants will be randomly asked to validate things among a large number of nodes. That is letting a small, random subset of validators decide whether the transaction should be accepted or rejected. Due to this system, you would need at least 80% of the Avalanche network to perform an attack.
What are subnets?
Subnets are smaller networks within a larger network. They are created by subnetting, which divides a larger network into smaller, more manageable parts. Subnets improve network performance, security, and manageability by limiting the size of network segments, establishing separate security zones, and assigning each subnet a unique network address.
Why Should You Use Avalanche for Your Own Blockchain Projects?
Avalanche consensus offers several advantages over other distributed ledger technology (DLT) protocols, such as proof-of-work (PoW), proof-of-stake (PoS), and delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS).
Avalanche consensus is faster and more scalable than traditional DLT protocols. By using a randomized, leaderless, and asynchronous process, Avalanche can achieve consensus quickly and efficiently. This allows for thousands of transactions per second to be processed on the network, compared to other blockchain platforms with lower transaction speeds.
Avalanche consensus provides a higher level of security and robustness for the network. The protocol ensures that all transactions are processed correctly and that validators are incentivized to act in the network’s best interest. This makes it more resistant to attacks, such as 51% attacks, compared to other consensus protocols.
The ability to shard the network through the p-Chain’s creation of subnets offers further scalability advantages. Sharding allows for increased throughput and reduced congestion on the network, enabling Avalanche to potentially scale beyond the current limits of other blockchain platforms.
Avalanche consensus offers flexibility to developers by allowing for the creation and management of new digital assets on the network. The c-Chain enables the creation of custom assets, such as tokens and smart contracts, which can be used for various use cases, such as DeFi, asset tokenization, and more.
In summary, Avalanche Consensus offers several advantages over other DLT protocols, including speed, scalability, security, and flexibility. The ability to shard the network and create custom assets through the p-Chain and c-Chain also provides further advantages that make Avalanche a promising platform for various use cases.
Avalanche holds the capacity to significantly transform the future of distributed ledger technology (DLT) by offering a swifter, more scalable, and enhanced secure platform for digital assets and applications.
With its unique consensus protocol, sharding capabilities, and flexibility for creating custom assets, Avalanche is poised to become a leading player in the DLT space.
Its faster transaction speeds and scalability make it more suitable for high throughput use cases such as financial transactions, gaming, and supply chain management. Additionally, its security features, including resistance to ‘51% Attack,’ make it a more secure platform for hosting digital assets. As the platform continues to mature and more developers and businesses adopt it, Avalanche is likely to play a significant role in shaping the future of DLT.
Avalanche looks promising platform for distributed ledger technology that offers several unique features and advantages over traditional blockchain protocols. Its consensus protocol, sharding capabilities, and flexibility for creating custom assets make it a highly scalable and secure platform for hosting digital assets and applications. As the platform continues to evolve and gain adoption, it is likely to play a significant role in shaping the future of DLT.
- Avalanche: https://support.avax.network/en/articles/6077308-what-are-the-differences-between-the-x-p-and-c-chains[↩]


