If you are a crypto enthusiast, you may have come across the term liquidity mining but are unsure about it. The most common investment approach in this field is HODLing, which means buying and keeping the assets in their wallets until the market prices rise.
However, there are many passive income ways to grow your assets. Liquidity mining is one of them. Following the boom of DeFi and DEX between the years 2017 and 2020, more than 130 DeFi platforms are successfully running and serving the swap options for over $100 billion worth of assets locked in them as of now, according to DeFi pulse. So, is it beneficial to put our assets here rather than HODL them? Here is a detailed guide on what it is and how it works.
What is liquidity mining?
Liquidity mining is a yield farming method, a passive way of earning by contributing to liquidity pools. You are getting rewarded with tokens according to the amount you are locking. So, you can ask us where I need to lock my assets or what the benefit is for them keeping our assets on our behalf. This is where you need to understand what are volatility and liquidity.
Crypto is a highly volatile market, and whenever a trader or an end-user wants to participate in a trade, sufficient funds must be available in the market. If you are going to the bank and want to withdraw a large amount of money that you have deposited for a longer period. The bank should be aware of this and must have that huge amount of money readily available whenever required.
Similarly, liquidity is the availability of assets in a market. Users who contribute to liquidity guarantee that there are sufficient assets accessible for trade, which can help lower price volatility and increase the market’s overall efficiency.
DeFi Terms Associated with Liquidity Mining
Before diving in, getting acquainted with the terms related to Liquidity Mining that we will discuss in this article is a good idea.
DEX
Unlike the centralized exchanges (eg: Binance or Coinbase), all operations of DEXes are decentralized and automated and facilitate Peer-to-Peer transactions efficiently with smart contracts. Your coins and tokens will be handled by you, and you own your private keys as well.
DEXes can be further divided into three categories. On-chain Order Books, Off-chain Order Books, and Automated Market Makers.
Order Books
Traditional exchanges use Order Books to proceed with transactions. If you want to buy/sell any assets, you can only proceed with that transaction, when another buyer or seller from another side quotes the same price to transact. Then the system will match both requests and will proceed with the transaction.
Automated Market Makers
As we have mentioned Order Books are for traditional exchanges. Have you ever thought of DEXes? Since Order Books is a very inefficient method, another buyer must wait for you to sell it at a particular price.
This is where Liquidity Pools and Automated Market Makers (AMM) come into play. AMM is a type of Decentralized Exchange. Instead of processing a trade with another buyer/seller waiting in line, users can process the trade with these algorithms.
AMMs buy and sell assets on a regular basis and profit from the gap between the highest buy offer and lowest sell offer. One great example of an AMM is Uniswap.
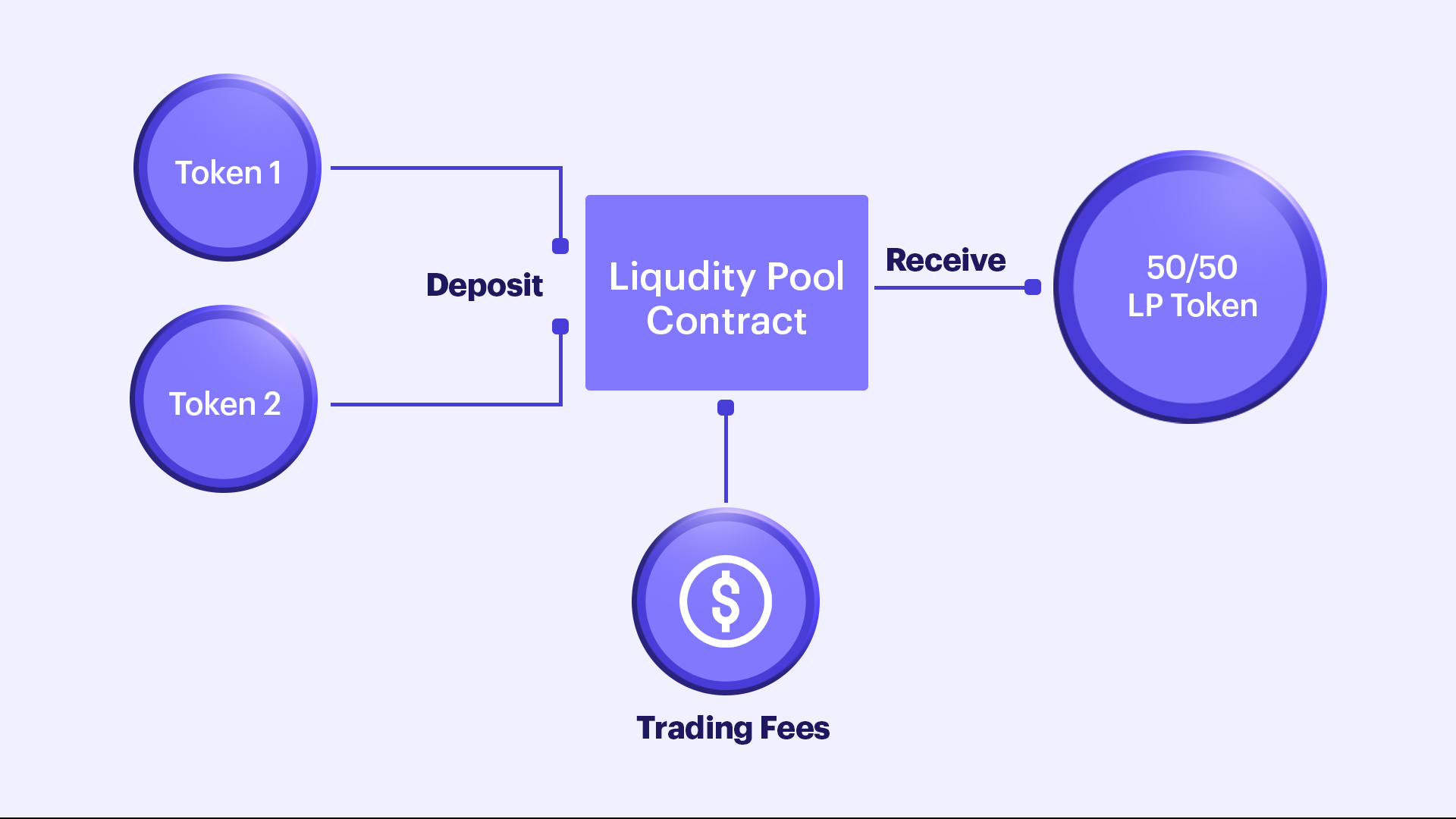
Liquidity Pools
These are the underlying concept of DEXes. As the education portal of Chainlink states,1
“Liquidity Pools are crowdsourced collections of crypto assets that the AMM uses to trade with people buying or selling one of these assets. The users that deposit their assets to the pools are known as liquidity providers (LPs).”
Simply put, liquidity pools are required to enable the liquidity of asset pairs so that those pairs can be traded. Every asset pair listed in the DEXes has its own liquidity pool; sometimes, a liquidity pool contains a pair of assets, and sometimes it may be more than two.
How Does it Work?
When a user subscribes and places his assets in the liquidity pool, those funds will be utilized to provide the liquidity of the particular asset/ asset pair. The user can earn a part of the money according to the amount he is locking in, which are charged as fees from the traders using the platform.
Some platforms pay the benefit amount in the form of APY (Annual Percentage Yield) or APR (Annual Percentage Rate), and some platforms feature reward incentives such as Governance tokens.
Those earnings are subjective and usually depend on,
- Size of the trading pool
- The overall trading volume of the particular asset pair
Once the user successfully locks up a pair of assets, they will be provided with LP tokens (Liquidity Provider tokens). Those are the proofs that you have locked your assets in. Risky and uncommon pairs usually offer higher APR. Stablecoin pairs are low risk, and their APR typically varies around zero percent.
The more a person owns an LP token, the more a share of the rewards will also increase.
Types of protocols
There are different types of liquidity mining protocols.
- Fair decentralization protocols: These protocols focus on developing a fair playing ground for all users and distributing native tokens equally among active users and early users.
- Progressive decentralization protocols
- Marketing-oriented protocols
Liquidity Mining vs. Yield Farming vs. Staking
- Yield Farming: A broad category of lending out assets and earning a passive income from them through fees and interests.
- Liquidity Mining: This is a form of yield farming but lending out the assets to the liquidity pools of the DEXes. By helping the DEXes provide liquidity for a particular pair, the liquidity provider earns a passive income through transaction fees every time another user swaps their token for another token inside that DEX.
- Staking: Refers to locking assets to help secure a blockchain network and validate transactions of PoS chains.
Benefits of Liquidity Mining
- Passive Income
- It is a great way of earning an amount rather than just HODLing your assets. It also comes with the potential for higher yields and as well as higher risks. That is directly proportional.
- Fair distribution of native tokens
- This concept of providing liquidity gives equal opportunity to individuals as well as institutional investors to obtain native tokens or governance tokens. These tokens give the voting power, with the ability to
- Vote on the development proposals for the ecosystem
- Vote on crucial changes to the protocol
- This concept of providing liquidity gives equal opportunity to individuals as well as institutional investors to obtain native tokens or governance tokens. These tokens give the voting power, with the ability to
Risk of Liquidity Mining
- Impermanent Loss
- One of the crucial risks associated with Liquidity mining is the possibility of price fluctuations.
- Rug pulls
- ‘Rug Pulls’ means that the core team behind that DeFi project ran away and disappeared with people’s money. This is a common scenario in the DeFi space, and putting your money into reliable projects is important.
- Chain.link: https://chain.link/education/defi/yield-farming[↩]


