Table of Content
In an era where urban centers face unprecedented challenges ranging from extreme weather events and rapid population growth to affordability crises and public safety concerns cities worldwide are increasingly turning to technology for solutions. While many envision smart cities with flying cars and robots, in reality, any city using sensors, such as on streetlights, is already “smart.” The concept of the “smart city” has evolved significantly over the past decade, driven by the need to enhance urban living and manage resources more effectively. By connecting infrastructure, cities can better manage resources and services. AI, including generative AI, offers new opportunities to improve services and efficiency but also brings new risks.
This article explores the current state and prospects of smart cities, examining how advancements in technology are reshaping urban environments. From recent developments and innovative products to the key risks and challenges associated with AI integration, we will delve into how smart cities are transforming our world and what lies ahead in this dynamic field.
The Rise of Smart Cities
A smart city is an urban area that leverages technology and data to enhance the quality of life, sustainability and efficiency of city operations. Local governments utilize smart city technologies such as information and communication technologies (ICT) and the Internet of Things (IoT). According to a recent Guidehouse Insights report, the global smart city technology market is projected to expand from $121 billion in annual revenue in 2023 to $301 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.7%. Total revenue over this period is anticipated to approach $2 trillion. 1
Evolving Smart Cities Landscape: Recent Developments and Innovations
The smart cities movement has fluctuated over the past decade, driven by evolving concerns over privacy and security and recent shifts in priorities due to the pandemic. It originally emerged from major tech companies aiming to introduce platform-as-a-service or city-as-a-service models.
In 2020, Ubicquia acquired the CityIQ smart city platform from GE Current, including its products, intellectual property, municipal contracts and employees. This acquisition will expand Ubicquia’s smart-city offerings, such as video monitoring for safety and traffic management. Meanwhile, GE Current will focus on LED lighting, Daintree connectivity and its LightGrid platform for outdoor lighting control. The CityIQ platform, previously used in smart-city projects like San Diego, did not align with GE Current’s core portfolio, prompting the sale. Ubicquia plans to integrate CityIQ with its existing smart-city solutions, scaling AI-powered services for cities. 2
Sidewalk Labs joined Google in 2021 and has developed products to make cities of the future more sustainable and equitable for all. For example, their product Mesa helps commercial buildings cut carbon emissions and recently added features like leak detection and air quality monitoring. These enhancements enable owners and tenants to prevent costly water damage and improve indoor comfort. MoMA PS1 in New York City has begun using Mesa to maintain ideal temperature and humidity for preserving its contemporary art installations. 3
Another product, Delve, assists real estate teams and cities in generating and comparing thousands of design options for urban blocks or neighborhoods. This year, Delve introduced new features that allow for rapid site evaluation, enhanced design generation using contextual data and analysis of a project’s sustainability and impact on neighborhood quality of life. 3
Sidewalk Labs also offers Pebble, a suite of parking solutions that helps cities and developers optimize parking needs, reducing the overall number of spaces and repurposing them for walkable neighborhoods. Sea Breeze Properties, for instance, used Pebble at their North City project in San Diego to create a dynamic parking system, encouraging fewer spaces for residents, employees, visitors and students. 3
CityNext is a global initiative, backed by Microsoft and its partners, aimed at building smart cities worldwide. The central component of the program is a website designed to help city leaders improve communication with citizens to enhance safety, health and well-being, offering ideas and inspiration to create an environment where governments, businesses and citizens can thrive. 4
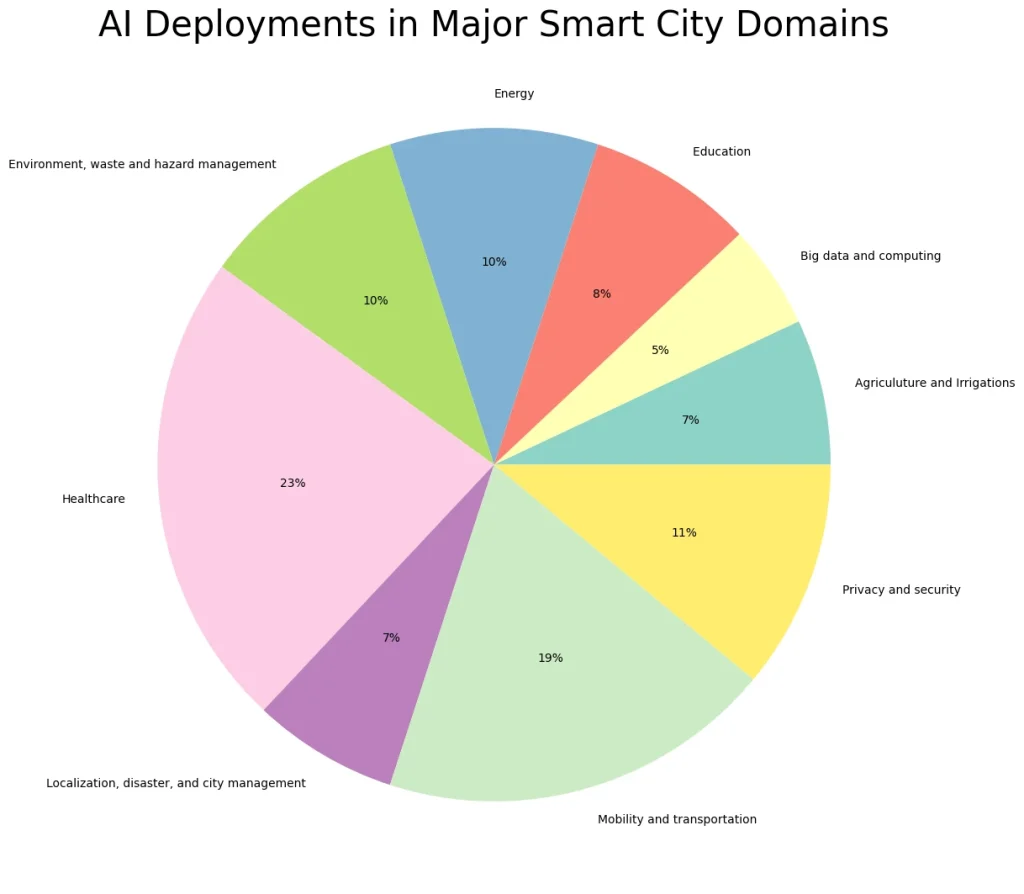
Key risks of AI-powered smart cities
Every technological advancement brings concerns about potential threats and unintended consequences, especially in cities and government agencies, where public services and sensitive data are involved. Key concerns include:
- Data privacy: The widespread use of sensors and surveillance in smart cities gathers vast amounts of personal data, raising privacy concerns. Several projects have been canceled due to community backlash over surveillance and transparency.
- Security and cyber resilience: Smart city systems’ interconnected nature makes them vulnerable to cyberattacks, which can risk public safety and economic stability. Cyberattacks on critical infrastructure can result in substantial losses.
- Digital equity and bias: The tech divide could leave older or low-income populations underserved by smart city initiatives. Ensuring equitable access to technology is essential to prevent widening gaps in access and services.
Addressing these risks will require proactive measures, including proper system design and guardrails for safe data usage. Despite the high enthusiasm for smart city initiatives, cautious adoption is warranted, with governments opting for a slow and deliberate approach to avoid potential pitfalls. 5
Shaping the Future: AI’s Impact on Smart Cities and the Path Forward
AI will shape smart cities in the next 5-10 years by enhancing digital government services, smart transportation and city modeling. AI may improve public services with tools like chatbots and personalized digital platforms for permits, taxes and healthcare. Smart transportation will benefit from AI-supported systems like autonomous vehicles, optimized traffic management and intelligent infrastructure. AI will provide virtual city models for planning and decision-making, such as predicting floods or managing power grids.
However, challenges remain, such as ensuring data transparency, community engagement and digital equity. To succeed, cities must balance AI’s potential with addressing public concerns about privacy and trust. Financial and public support will be key to making smart city projects sustainable and beneficial for all.
The smart city market is poised for significant growth, with investments in technology projected to surge. Innovations from companies like Ubicquia and Sidewalk Labs demonstrate the evolving landscape of smart city solutions, from enhanced safety and efficiency to sustainable urban planning. Initiatives like Microsoft’s CityNext further highlight the global push towards creating environments where technology fosters community well-being.
As cities become smarter, policymakers, industry leaders and communities need to work together carefully and thoughtfully. By prioritizing ethical use, sustainability and resilience, AI can lead to a new era of urban prosperity, ensuring that smart cities benefit everyone and pave the way for a better quality of life for future generations.
- AI and Smart Cities: https://cities-today.com/smart-city-market-to-reach-300-billion-by-2032/[↩]
- AI and Smart Cities: https://www.ubicquia.com/news/ge-current-sells-cityiq-platform-smart-cities-ubicquia[↩]
- AI and Smart Cities: https://blog.google/outreach-initiatives/sustainability/how-sidewalk-labs-is-helping-make-cities-more-sustainable-in-2022/[↩][↩][↩]
- AI and Smart Cities: https://metia.com/work/microsoft-citynext/[↩]
- AI and Smart Cities: https://www.spglobal.com/en/research-insights/special-reports/ai-smart-cities[↩]


