Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the healthcare industry, driving remarkable progress in patient care, diagnostics, and treatment methodologies. AI technologies, such as machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics, are redefining efficiency and accuracy in multiple medical domains. The AI healthcare market is projected to reach $45.2 billion by 2026 1, highlighting its rising significance and potential influence on global health systems.
AI is crucial in the healthcare market due to the rise in big data, rising costs, and personalized medicine demand. AI-powered systems analyze vast datasets, predict patient outcomes, and streamline administrative processes, improving patient care and reducing operational costs. Morgan Stanley reports that AI applications could save the industry $150 billion annually by 2026 due to enhanced efficiency and precision. 2
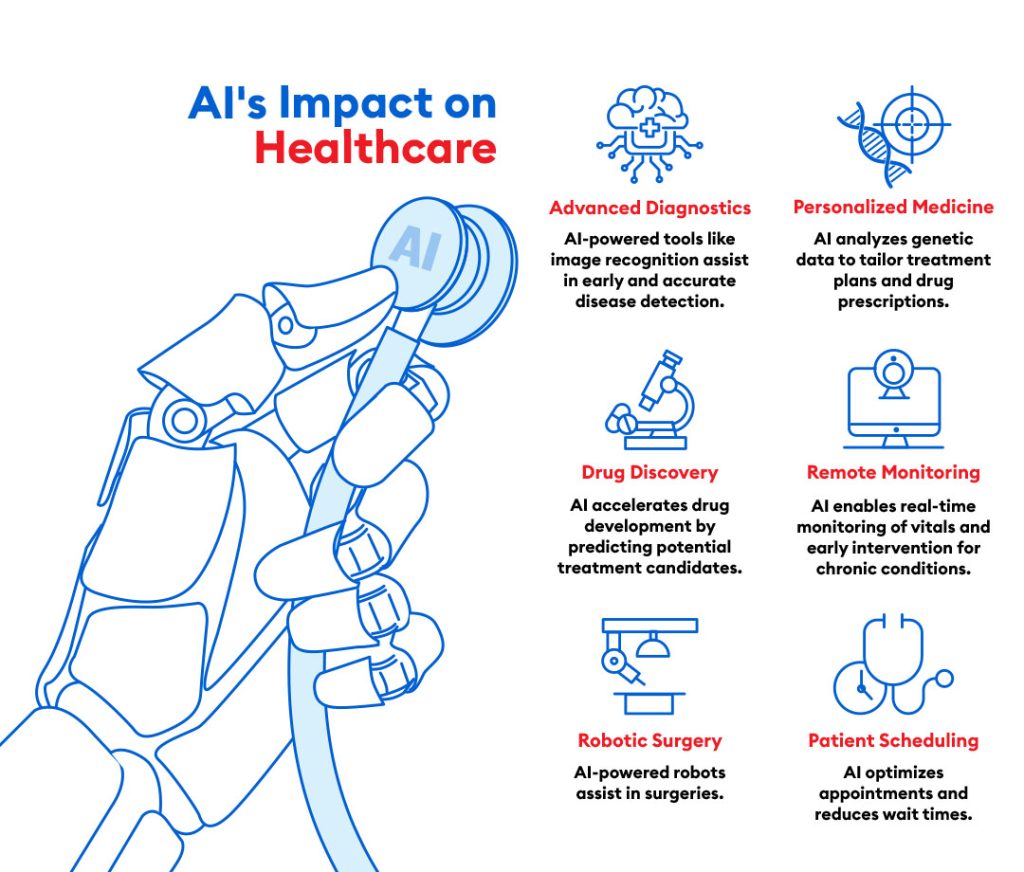
Current Landscape of AI in Healthcare
In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of AI, underscoring its significance in effectively handling public health emergencies. AI’s rapid analysis and interpretation of large volumes of data have been crucial in developing vaccines, monitoring patients, and allocating resources, showcasing the importance of digital solutions and telehealth. These successes generated a lot of excitement in the industry, showcasing the advantages of integrating AI/ML to enhance patient outcomes more efficiently than conventional approaches.
The demand for telehealth continues to be resilient even in the post-COVID-19 era.
AI technologies are being utilized in healthcare for diagnosis, patient management, and personalized medication and care. Diagnosis uses tools like radiology and medical imaging, while patient management involves managing patient records, preventing errors, monitoring treatment, and supporting treatment decisions. 3 Personalized medication and care services diagnose medical conditions, manage patient health, and adjust dosages.
AI-powered diagnostic tools have reshaped the way diseases are detected and treatment plans are developed. Google DeepMind built an AI system that can accurately diagnose more than 50 eye diseases 4, performing at the same level as top ophthalmologists. This AI system utilizes optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans to detect and diagnose conditions like age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy5. Their system is designed to not only detect eye diseases but also prioritize urgent cases. By doing so, they aim to reduce the time to treatment and prevent sight loss in critical situations.
AI is transforming surgical procedures alongside. The da Vinci Surgical System exemplifies the cutting-edge technology of AI-driven robotic surgery, enabling highly precise and minimally invasive procedures. This technology significantly improves the surgeon’s abilities, resulting in shorter recovery periods and decreased chances of complications.6 With their ability to offer a meticulous perspective of the surgical area and facilitate accurate maneuvers, these robotic systems greatly enhance patient outcomes.
AI and IoT are revolutionizing remote patient monitoring (RPM) by enabling real-time tracking of patient vitals, medication adherence, and early detection of potential health issues 7. These technologies are particularly useful for managing chronic conditions, reducing hospital readmissions, and improving patient outcomes.
AI algorithms analyze data from wearable devices and sensors to provide personalized insights and alerts, aiding in early intervention for conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and mental health disorders.
IoT-enabled devices like smart pill dispensers and fall detection sensors further enhance patient safety and treatment adherence. AI is also revolutionizing genomics by enabling personalized medicine by analyzing large genetic data sets, identifying patterns, and predicting individual patient responses to specific treatments 8.
Technological Innovations and Breakthroughs in Healthcare
The healthcare landscape has been dramatically shifted by recent advancements in AI technologies, including machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision. In 2024, the integration of AI into patient care has resulted in significant advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and personalized medicine.
An astonishing example is the integration of AI-powered diagnostic tools at Mayo Clinic in 2023. With the power of computer vision, these tools can analyze medical images with exceptional precision, often outperforming human radiologists 9. This technology has played a crucial role in the early detection of cancer, resulting in timely interventions and better patient outcomes.
AI has redefined personalized medicine by creating precise healthcare models for individual patient profiles. Stanford Health Care uses NLP algorithms to analyze electronic health records, predicting treatment responses, specifically effective in managing chronic diseases like diabetes. This approach has improved patient adherence and health outcomes since 2023. 10
The role of AI in drug discovery and development has been truly remarkable. Insilico Medicine utilizes machine learning to make accurate predictions about molecular behavior and discover promising drug candidates. This cutting-edge technology reshaped the development of a groundbreaking treatment for fibrosis in 2023, significantly shortening the timeline from discovery to clinical trials. 11
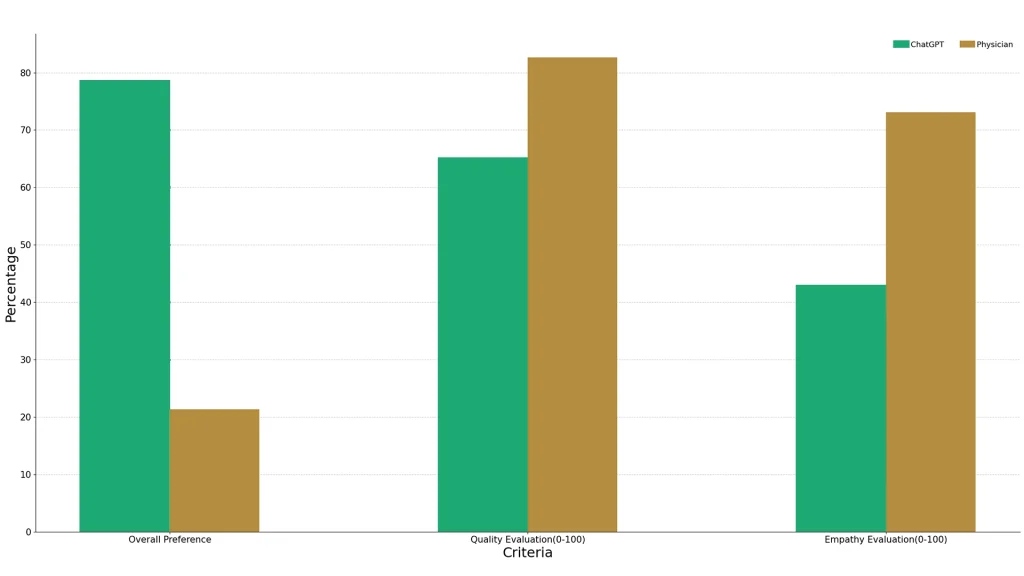
Key Factors Driving AI Adoption in Healthcare
Exponential Increase in Healthcare Data:
The sheer volume of data generated by the healthcare industry is staggering. In 2020, experts predicted that the healthcare industry would produce an enormous quantity of data – a mind-boggling 2.3 zettabytes, equivalent to 2,300,000,000,000,000,000,000 bytes. 12 Advanced AI technologies are crucial for effectively analyzing and working with the massive amount of data available. That enables dealing with large datasets and extracting valuable insights that can be put into action.
Cost Reduction:
Accenture predicts that the implementation of AI in the U.S. healthcare system could result in annual savings of up to $150 billion by 2026. 13 This would be achieved by improving efficiency and making better use of resources. AI-driven diagnostic tools have a remarkable impact on operational costs by reducing the time and costs typically associated with traditional diagnostic methods.
Improved Patient Outcomes:
AI technologies have shown remarkable advancements in patient outcomes. As an illustration, AI models at the Mayo Clinic have the unique capacity to identify pancreatic cancer on CT scans a year before it is clinically diagnosed. 14 This early detection enables timely intervention and significantly enhances patient outcomes.
Investment and Innovation:
The healthcare AI market was valued at USD 1.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 29.8 billion by 2033, according to a report by Spherical Insights & Consulting. The market is expected to see significant innovation and returns, with health-tech incubators and accelerators providing startups with resources and mentorship. 15
Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring:
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the use of telemedicine, with AI enhancing its capabilities. AI-powered platforms enable real-time patient monitoring, predictive analytics, and personalized treatment plans, making healthcare more accessible and efficient. A 2023 Deloitte study suggests this could reduce hospital visits. 16
The integration of AI in healthcare is driven by the need to manage vast data, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes. The sector is experiencing significant growth and investment, with AI technologies enhancing diagnostics and personalized treatment plans. The future holds substantial economic benefits and transformative improvements in patient care.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Healthcare
Data Privacy:
The European Union’s 2023 reinforcement of GDPR has emphasized the importance of data privacy in healthcare, mandating stricter measures such as more stringent consent requirements and data anonymization techniques to safeguard patient privacy. 17 However, despite these measures, AI’s ability to de-anonymize data poses a continuous threat to privacy. 18
The FDA in the U.S. is developing a flexible regulatory framework to accommodate AI advancements, including guidelines for adaptive algorithms. However, the EU’s comprehensive approach often imposes significant regulatory burdens, which can hinder innovation in AI healthcare, despite its comprehensive approach. 19
High Costs:
The exorbitant expenses linked to developing and integrating AI systems can pose a significant barrier for numerous healthcare providers. These costs encompass not just the initial investment in technology, but also the ongoing expenses tied to data management, system updates, and compliance with regulatory requirements. 19Smaller healthcare providers, in particular, might find it difficult to afford these investments, which hinders the widespread adoption of AI.
Bias in AI Algorithms:
Biased AI algorithms can result in unfair treatment outcomes. A study conducted in 2023 found that certain AI diagnostic tools exhibited lower accuracy rates when used on minority populations. 20This discrepancy can be attributed to biased training data. This problem stems from long-standing biases in the data used to train AI models, which have the potential to perpetuate and worsen healthcare disparities.
Ethical Guidelines and Frameworks:
Implementing ethical guidelines and frameworks is crucial for promoting the responsible use of AI in the health industry. In 2023, the World Health Organization established guidelines prioritizing patient safety, fairness, and accountability. These frameworks are essential for guiding the development and deployment of AI technologies, ensuring they benefit all patients fairly and equitably. 21
Future Prospects and Predictions in Healthcare
Personalized Medicine and Predictive Analytics:
By 2030, AI is expected to significantly impact healthcare delivery, particularly in personalized medicine and predictive analytics. This technology will enable precise treatments based on individual genetic profiles and real-time health data, improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes. AI-powered predictive care could potentially reduce chronic diseases. 22
Remote Patient Monitoring:
AI has the potential to turn around remote patient monitoring, enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of telemedicine. AI-powered platforms offer ongoing patient monitoring, instant health analytics, and customized treatment plans. 23 This will enhance patient engagement and decrease the necessity for hospital visits, resulting in substantial cost savings and improved management of chronic conditions.
Advancements in Drug Discovery:
Emerging technologies, such as quantum computing and advanced neural networks, exhibit the promise of transforming the field of drug discovery. Startups such as Tempus and Owkin are utilizing AI to expedite the drug development process, streamlining clinical trials and decreasing the time it takes to bring new therapies to market. 24These advancements are poised to revolutionize the medical field, delivering cutting-edge treatments to patients with greater speed and efficiency.
Societal Impact:
AI in healthcare will significantly impact society, democratizing access to high-quality care, particularly in underserved areas. Telemedicine, enhanced by AI, will become ubiquitous, ensuring continuous patient monitoring and proactive care management. 25As AI technologies evolve, they will make healthcare more effective, efficient, and accessible.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing the the medical sector by improving diagnostics, patient care, and operational efficiency. The integration of technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics is driving advancements in personalized medicine, remote patient monitoring, and telehealth. AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets, predict patient outcomes, and streamline administrative processes is crucial for improving patient care and reducing operational costs. Despite challenges like data privacy concerns, regulatory hurdles, high costs, and potential biases in AI algorithms, the benefits of AI in reducing costs and improving patient outcomes are undeniable. The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the value of AI in handling public health emergencies, accelerating vaccine development, and enhancing telehealth services. The future of AI in the medical field holds great promise in drug discovery, predictive analytics, and personalized treatments.
- AI and Healthcare: https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2021/04/28/the-current-state-of-the-healthcare-ai-revolution/[↩]
- AI and Healthcare: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7325854/[↩]
- AI and Healthcare: https://www.bsr.org/reports/BSR-AI-Human-Rights-Healthcare.pdf[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://www.aao.org/education/headline/google-s-ai-product-detects-retinal-diseases-with-[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://deepmind.google/discover/blog/a-major-milestone-for-the-treatment-of-eye-disease/[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://www.medicaldevice-network.com/news/googles-deepmind-ai-can-accurately-detect-eye-diseases/[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://medtechintelligence.com/column/ai-driven-continuous-remote-patient-monitoring-crpm-empowers-telehealth/[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://www.intuz.com/blog/iot-in-remote-patient-monitoring[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/mayo-clinics-ai-innovation-inspires-hope-in-early-detection-of-pancreatic-cancer/[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://stanmed.stanford.edu/translating-ai-concepts-into-innovations/[↩]
- AI and Healthcare: https://shorturl.at/8bCVu[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2024/01/how-to-harness-health-data-to-improve-patient-outcomes-wef24/[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://www.accenture.com/au-en/insights/health/artificial-intelligence-healthcare[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://medcloudinsider.com/articles/2023/10/02/mayo-clinic-hidden-cancers.asp[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://finance.yahoo.com/news/global-generative-artificial-intelligence-ai-050000828.html?guccounter=1&guce_referrer=aHR0cHM6Ly93d3cuZ29vZ2xlLmNvbS8&guce_referrer_sig=AQAAAJ9Bm8-uWeqvqccWZqIwFwWbXV6EcaYG-oJp9GGenxuNQkPZhV2BG66zodTSOgPiofGhNXP0GZNKmVLfvPYR6wxEv7nnJRHEq14y8GkGurTX6FyzH3WmrTfDQbzdtAwX9VN0ZKjGDu2AqyfDTmsgr2iekUZRO1uFOBlaiPS9Y3_B[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://www.deloitte.com/global/en/Industries/life-sciences-health-care/analysis/global-health-care-outlook.html[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/14/2/675[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://bmcmedethics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12910-021-00687-3[↩]
- AI and health industry: https://law.stanford.edu/2024/04/06/eu-and-us-regulatory-challenges-facing-ai-health-care-innovator-firms/[↩][↩]
- AI and health industry: https://www.theregreview.org/2023/06/01/katz-a-new-balance-between-health-care-privacy-and-artificial-intelligence/[↩]
- AI and Healthcare: https://shorturl.at/WC8Xr[↩]
- AI and Healthcare: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/01/future-of-artificial-intelligence-healthcare-delivery/[↩]
- AI and Healthcare: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/healthcare/our-insights/transforming-healthcare-with-ai[↩]
- AI and Healthcare: https://augnito.ai/resources/5-startups-championing-ai-in-drug-discovery/[↩]
- AI and Healthcare: https://adamfard.com/blog/ai-healthcare-startups[↩]


