Table of Content
- 1. AI-Powered Cyber Attacks:
- 2. Rise of Nation-State Threats:
- 3. Ransomware and Phishing Scams:
- 4. Supply Chain Attacks and IoT Vulnerabilities:
- How AI is Elevating Cybersecurity Measures
- Beyond Tools: Cybersecurity Management
- Trends in Cybersecurity Shaped by AI
- Strategic Implications for Investors
- Graph Citations:
The threats associated with cybersecurity today are far more widespread than they were in the past. In today’s digital era, transactions and communications are predominantly conducted online, giving rise to increasingly complex cybersecurity challenges. Presently, there are several hazards that one must be aware of, including ransomware attacks, phishing schemes, AI-powered attacks, vulnerabilities in IoT devices, worries over cloud security, and state-sponsored cyberwarfare. 1
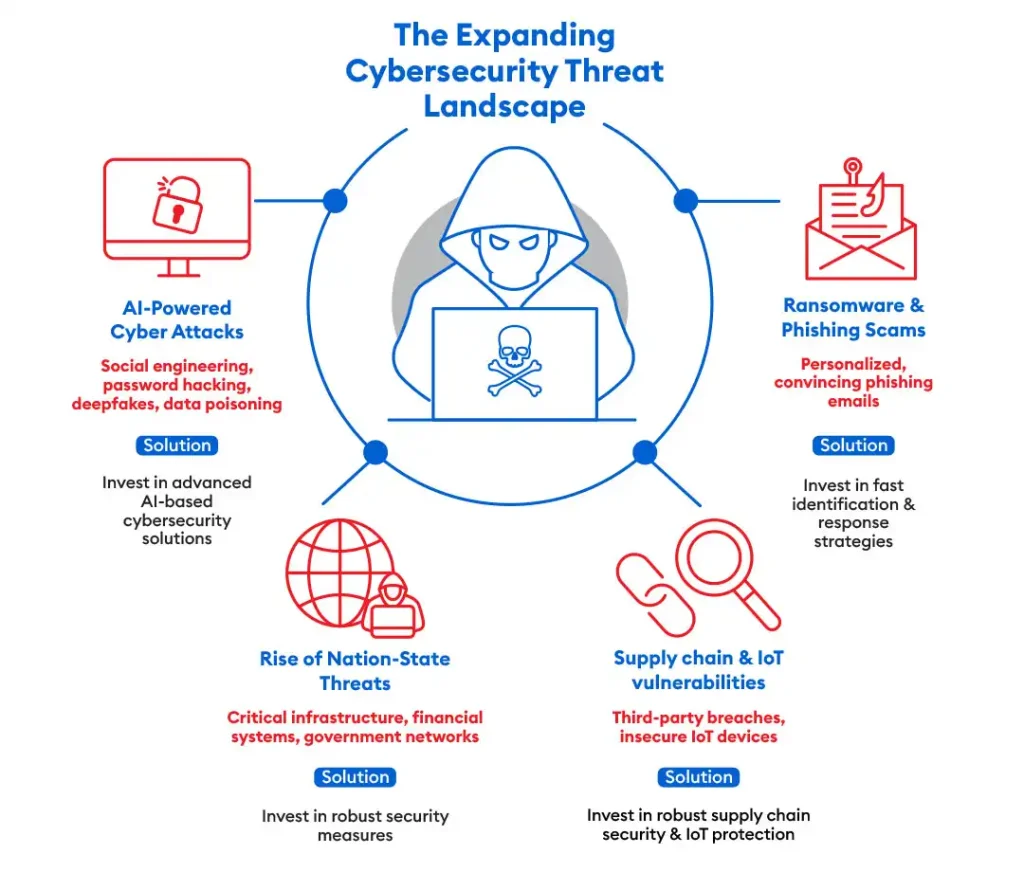
Cybersecurity threats have evolved in both scale and sophistication. Modern attackers utilize advanced techniques, including AI, to exploit vulnerabilities and execute highly targeted attacks. For investors, recognizing the breadth of these threats is essential for evaluating the resilience of potential investments.
1. AI-Powered Cyber Attacks:
Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging AI to enhance the effectiveness of their attacks. AI can automate social engineering schemes, refine password-hacking techniques, create convincing deep fakes, and execute data poisoning attacks. This escalation in AI-driven threats requires equally sophisticated defensive measures, making companies that invest in advanced AI-based cybersecurity solutions more attractive to investors. 2
2. Rise of Nation-State Threats:
State-sponsored cyberattacks are on the rise, targeting critical infrastructure, financial systems, and government networks. These attacks pose a serious risk to economic stability and national security since they are frequently well-funded and highly sophisticated. 3
3. Ransomware and Phishing Scams:
These traditional threats have become more sophisticated with AI, enabling attackers to craft highly personalized and convincing phishing emails. Businesses that can identify and address these issues fast are in a better position to safeguard their resources and reputations, which makes them more dependable investments. 4
4. Supply Chain Attacks and IoT Vulnerabilities:
As supply chains and IoT devices become more integrated into business operations, they also become prime targets for cyberattacks.
Supply chains are becoming a more attractive target for cybercriminals, who use weaknesses in third-party providers to breach larger networks. This trend highlights the need for robust third-party risk management strategies. There are vulnerabilities brought about by the growth of IoT devices and operational technology (OT) systems. Since these gadgets frequently lack strong security safeguards, hackers attempting to breach networks or do physical harm find them appealing targets. 5
Investors should focus on companies with robust supply chain security measures and IoT protection protocols, as these firms are less likely to suffer significant disruptions from such attacks.
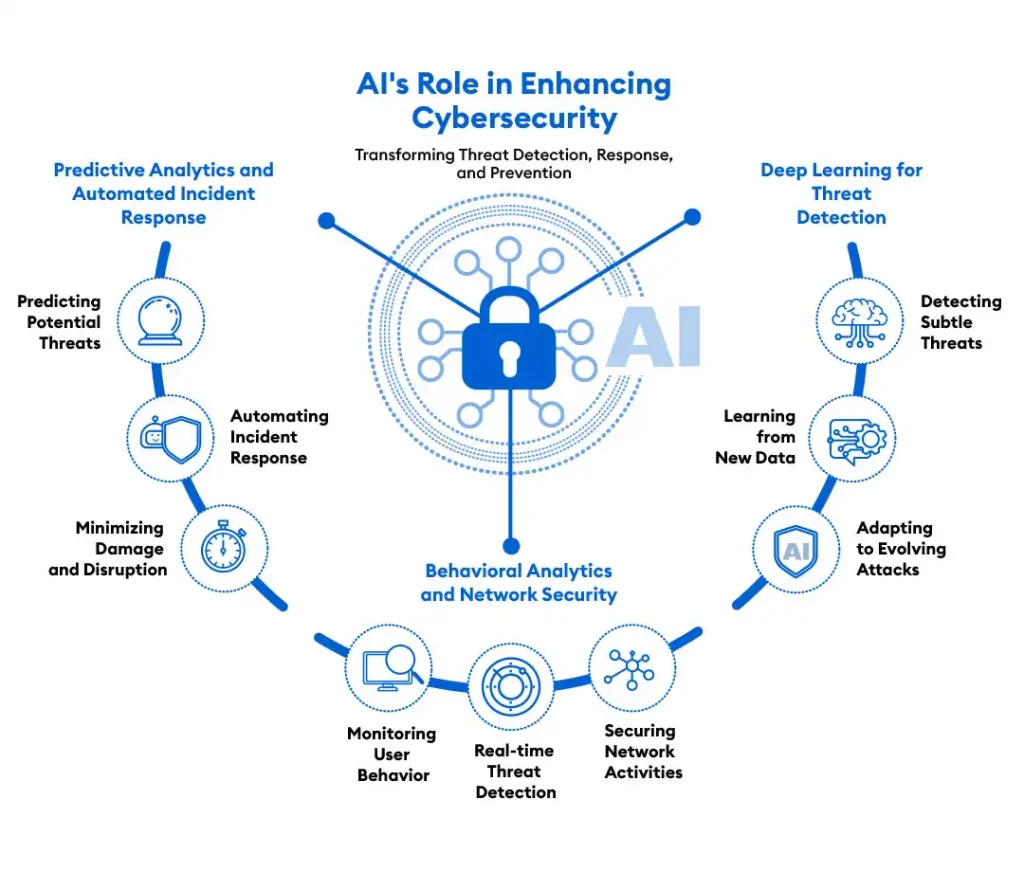
How AI is Elevating Cybersecurity Measures
AI is transforming cybersecurity by automating complex detection and response tasks, learning from past incidents to improve defenses, and providing predictive analytics. The integration of AI into cybersecurity practices offers several critical benefits:
1. Predictive Analytics and Automated Incident Response:
AI can analyze vast amounts of data to predict potential threats and automatically respond to incidents. This proactive approach reduces threat detection and response time, minimizing damage and operational disruption. Investors should seek companies that leverage AI for predictive analytics and automated incident response to ensure quicker and more effective threat mitigation.
2. Behavioral Analytics and Network Security:
AI enhances cybersecurity by monitoring user behavior and network activity to identify anomalies that may indicate a breach. These capabilities allow real-time threat detection and response, providing a significant security advantage. Firms that employ advanced behavioral analytics will likely experience fewer successful attacks, making them safer investments.
3. Deep Learning for Threat Detection:
Deep learning techniques improve the detection of subtle and sophisticated threats, such as zero-day exploits. By continuously learning from new data, AI systems can identify previously unknown threats and adapt to evolving attack patterns. Companies utilizing deep learning for cybersecurity can better protect their assets, offering greater security and stability to investors.
Beyond Tools: Cybersecurity Management
Having the appropriate tools is only one aspect of cybersecurity; another is efficiently managing your technological estate. Strict controls are necessary to implement a solid cybersecurity policy and strategy.
1. Comprehensive Risk Management:
Effective cybersecurity management requires a comprehensive approach to risk management. This includes identifying and prioritizing risks, developing mitigation strategies, and continuously monitoring for new threats.
Data breaches have ramifications beyond only technical issues. The regulatory landscape continually evolves, with stricter data protection and privacy laws enacted worldwide. Companies must navigate these changes to avoid costly fines and legal repercussions. AI can help automate compliance processes, monitor regulatory changes, and ensure adherence to industry standards. Investors should prioritize firms with strong compliance management capabilities to mitigate regulatory risks. 6
2. Belief in the Cyber Sector – Combating Misinformation:
Deepfakes, social media manipulation, and false information erode digital content’s credibility. It gets harder to tell reality from fantasy as cyber dangers change. Investors and other stakeholders must learn how to navigate the murky waters of disinformation successfully. 2
3. Incident Response and Recovery:
A well-prepared incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of cyberattacks. This plan should include clear protocols for detecting, responding to, and recovering from incidents and regular drills to ensure readiness. 7
4. Employee Training and Awareness:
A major contributing component in many cyber incidents is still human error. Frequent training and awareness initiatives can lower the likelihood of successful assaults by assisting staff members in identifying and addressing such risks. 8
Trends in Cybersecurity Shaped by AI
Unquestionably, AI is still significantly impacting cybersecurity, and as it develops, it will continue to revolutionize this industry. The use of AI in cybersecurity has produced better results and allowed for the emergence of fresh trends that will influence the direction of digital security as we advance. These patterns show how sophisticated cyberattacks are becoming and how much more refined and proactive security measures are required.
1. Transition to Preventive Defense:
AI enables a shift from reactive to proactive cybersecurity measures. Predictive analytics can identify risks and vulnerabilities before they are exploited, reducing the likelihood of breaches. Companies adopting proactive defense strategies are likely to experience fewer security incidents, providing greater stability for investors. 9
2. Zero Trust Security Models:
AI plays a key role in adopting zero-trust security models, which assume that threats can originate both inside and outside the network. AI helps enforce strict access controls and continuously monitors user behavior to detect potential threats. 10
3. AI-Powered Identity and Access Management:
User behavior analysis and anomaly detection that suggests compromised credentials, enhances identity and access control. This lowers the possibility of unwanted access and improves the security of access restrictions. AI can create thorough audit trails, enforce access limits, and monitor compliance infractions by examining user behavior and access patterns. Noncompliance reduces the potential legal and financial ramifications by assisting companies in adhering to data protection laws like the GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. With AI’s ability to closely regulate access and learn from user behavior, organizations may more accurately and efficiently comply with regulatory standards. 11
Strategic Implications for Investors
The development of AI in cybersecurity reflects a broader trend of using technology to counteract rapidly evolving threats. AI’s ability to gather and analyze threat intelligence, automate responses, and enhance compliance is transforming the cybersecurity landscape. Understanding these advancements and their implications is crucial for investors to identify companies with robust cybersecurity strategies poised for growth and resilience. As AI evolves, its strategic importance in cybersecurity will only increase, making it a critical consideration for investment decisions in the digital era.
Graph Citations:
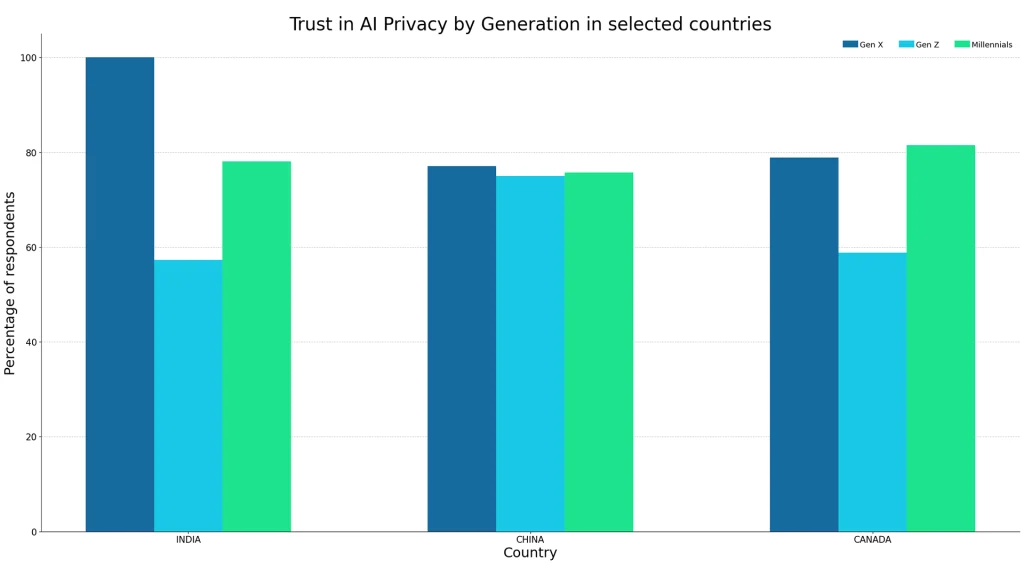
Trust in AI Privacy by Generation in Selected Countries:
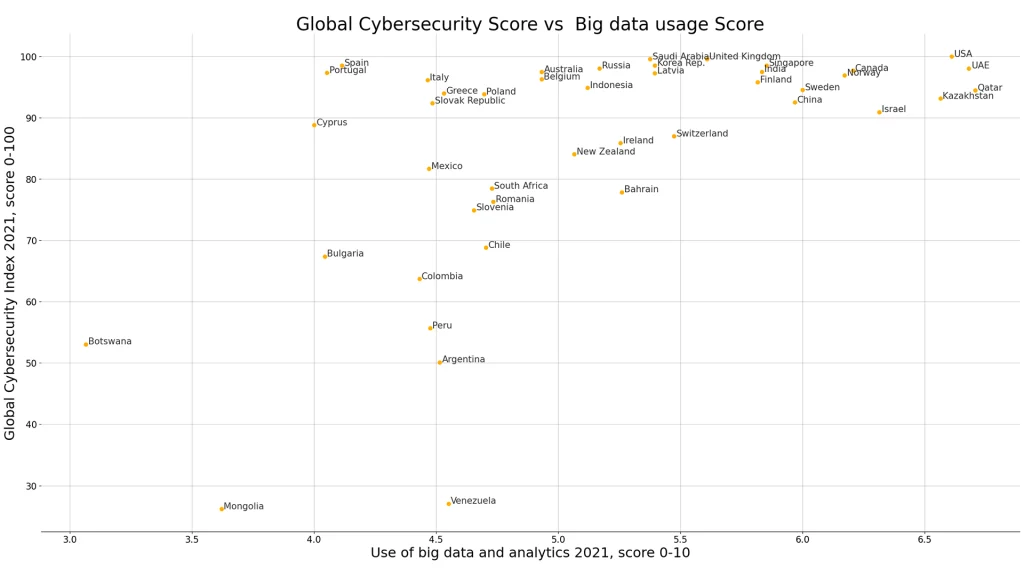
Global Security Score vs Big Data Usage Score:
- Artificial Intelligence and Big Data for Cybersecurity in Enterprise Data Management (2024). Retrieved from Mendeley Data. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
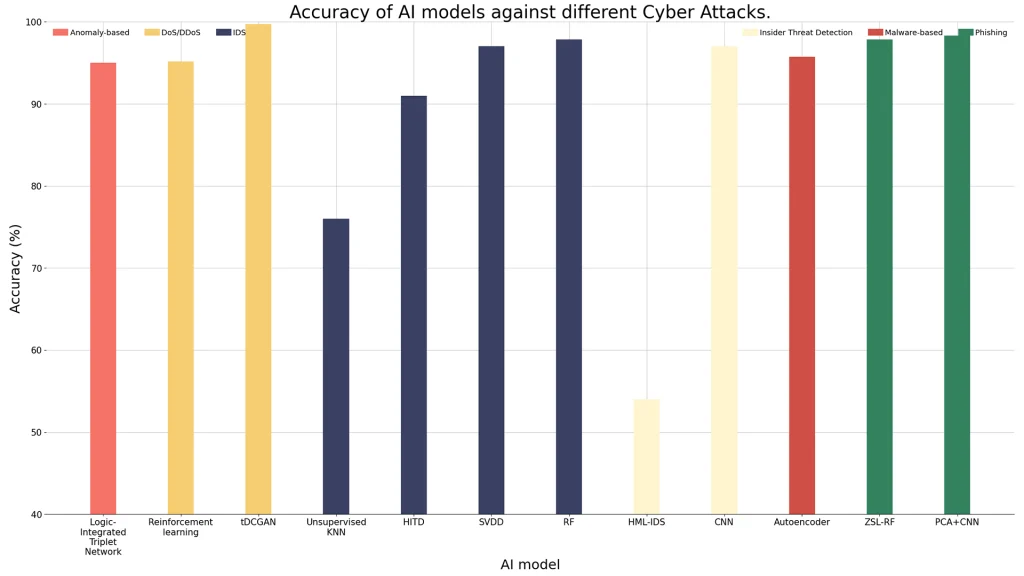
Accuracy of AI Models Against Different Cyber Attacks:
- Comparative Evaluation of AI-Based Techniques for Zero-Day Attacks Detection (2024). Retrieved from MDPI. Open Access Article.
- AI and Cyber security: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.927398[↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://www.morganstanley.com/articles/ai-cybersecurity-new-era[↩][↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.1772[↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://www.metacompliance.com/blog/phishing-and-ransomware/how-ai-enables-sophisticated-phishing-attacks[↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://www.consultancy.uk/news/35847/cybercriminals-continue-to-target-supply-chain-weaknesses[↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://blogs.lse.ac.uk/impactofsocialsciences/2024/04/15/new-data-protection-and-privacy-laws-have-changed-the-regulatory-landscape-for-researchers-in-the-global-north/[↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://www.dataguard.co.uk/cyber-security/incident-response-plan/[↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://blog.usecure.io/the-role-of-human-error-in-successful-cyber-security-breaches[↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://secureframe.com/blog/how-will-ai-affect-cybersecurity[↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://www.crowdstrike.com/cybersecurity-101/zero-trust-security/[↩]
- AI and Cyber security: https://www.crowdstrike.com/cybersecurity-101/identity-protection/machine-learning-and-ai-in-iam/[↩]


