The digital age has changed how we live and operate. From social media to e-commerce, the digital world has given us access to information and opportunities previously limited to a selected few. With its vast array of uses outside of currency and payments, the digital economy is now called the Blockchain Economy. The blockchain is a type of ledger that is automated, transparent, and decentralized. It lists all the transactions (or records) made on an encrypted database or shared network. Its value lies in its ability to form an unchangeable record of transactions that everyone in the network verifies without any central controlling authority.
This blog post will provide an understanding of blockchain, including its various use cases and its developing ecosystem.
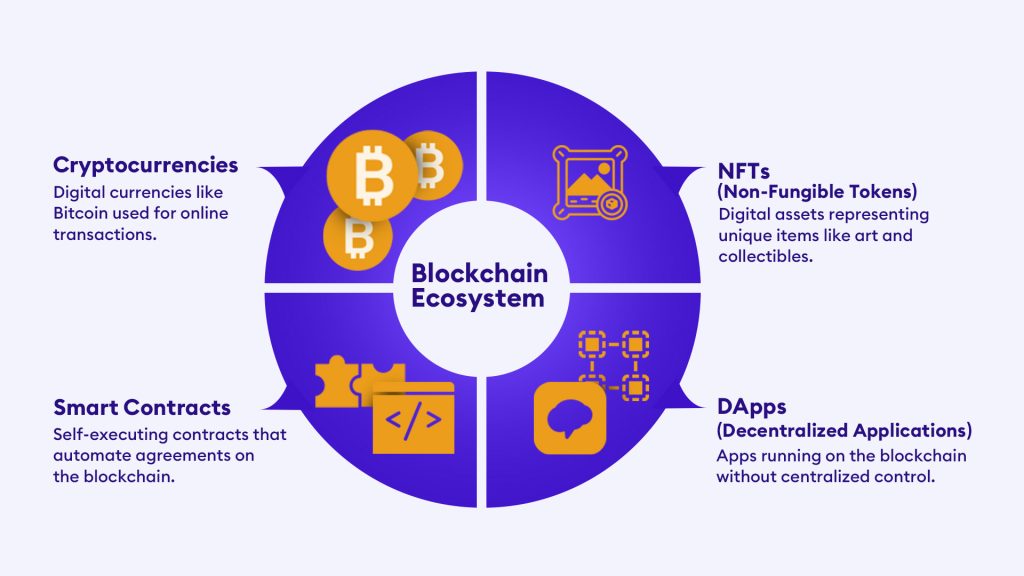
What is Blockchain Technology?
A Blockchain is a distributed network that keeps a continuously growing record of all transactions across many computers. It is an incorruptible digital ledger that can record transactions without a central authority. This type of distributed ledger has many potential applications, including in finance, supply chains, and healthcare.
Use Cases of Blockchain
- Digital Assets: You can use Decentralized Network to track assets, verify authenticity, and transfer ownership. This use case can help verify and track the authenticity of goods, improve supply chain visibility, and reduce fraud.
- Distributed Ledger: Enterprises dealing with IT assets, as well as real estate, aircraft, and automobiles, can benefit from using a distributed ledger, which can help minimize expenses and risks.
- Big Data: For example, a healthcare company could use the blockchain to store medical data so it is easier to access and find. This could reduce the costs of data storage and increase efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Companies could use the blockchain to store data about their supply chain and verify authenticity. This could prevent counterfeit goods, increase transparency, and reduce fraud.
- Smart Contracts: You can develop smart contracts using blockchain technology. This can reduce contract fraud, help trace and enforce agreements, and reduce asset tracking costs. Smart contract technology is still in its infancy, but it has the potential to change the way we transact and do business with each other.
Advantages
- Transparency: Transparency is a significant advantage of Decentralized Network technology, enabling transactions to be fully transparent without intermediaries. This implies that all participants on the network can verify all transactions.
- Immutability: Another advantage of Decentralized Network is immutability. This means that records cannot be changed or deleted once added. This provides complete accuracy and security.
- Decentralization: The last advantage of blockchain is decentralization. Transactions are made and stored by computers across the network rather than by a central authority. This means the network is decentralized, and there is no single point of failure.
- Security: The security of the blockchain is based on cryptography. This means that the system is secure and there is no way to tamper with the data without getting access to the encrypted distributed ledger.
Disadvantages
- Cost: By leveraging decentralized networks, blockchain technology can potentially reduce transaction costs and streamline business operations by removing the need for a central authority to verify transactions. Furthermore, the absence of intermediaries reduces costs and third-party fees, as no individual or company controls the information. Nonetheless, the current limitations in scaling up blockchain operations lead to increased transaction costs in specific scenarios. Regardless, new blockchain initiatives aim to tackle these challenges while established platforms like Ethereum continue to develop and enhance their technology to meet increasing demand.
- Scalability: The current Decentralized Network technology infrastructure can only handle a few transactions per second, limiting its scalability.
- Security Issues: Another common disadvantage of blockchain is security issues. This is because the technology is relatively new, and relatively fewer experts are familiar with it. This can lead to slower development and a higher risk of vulnerabilities.
- Rise of New Firms: The third disadvantage of Decentralized Network is that it can increase the competition in the market between firms that use the technology. This can lead to a fall in profit margins, higher costs, and possible market saturation.
- Privacy concerns: Some Decentralized Network networks are public, meaning all data is available for anyone to see. This lack of privacy can be an issue for sensitive information and transactions.
Best Practices for Deploying Applications
- Focus on Scalability: The challenge of scalability is among the most significant issues facing blockchain technology. Its current limitations make it unable to cope with the transaction volume needed by large organizations such as banks. Despite this, blockchain presents significant potential for scalability, making it an appealing alternative for developing nations, which require more effective governance and economic systems.
- Seek Variety in Partners: With over a decade of development, Decentralized Network is a technology poised to revolutionize the world, already adopted by significant industries like finance, insurance, and supply chain management. Collaboration through partnerships is an essential aspect of Decentralized Network development. It takes various forms, such as joint development between companies or utilizing blockchain developed by another company to address their challenges. The potential of blockchain development relies on partnerships between companies and developers, combining expertise and resources to create innovative solutions.
- Be Viable: It is crucial to evaluate if your blockchain business is viable. If it isn’t profitable, consider whether it is worth investing more time and resources. The last best practice is considering whether your blockchain business is viable. If it isn’t profitable, consider whether it is worth investing more time and resources.
- Understand the legal and regulatory environment: Blockchain technology is still relatively new, and there needs to be more precise regulations and guidelines. Therefore, understanding the legal and regulatory environment in which the application will be deployed is essential.
Final Words: Wrapping Things Up
This article has covered various Decentralized Network-related topics, including its definition, different use cases, and the evolving ecosystem surrounding it. Additionally, we have explored the advantages and disadvantages of Decentralized Network, along with best practices for implementing Decentralized Network applications. Finally, we conclude with our thoughts on the nature of Decentralized Network. We trust this article has provided valuable insights into this technology.

