Imagine a market where you usually go to buy groceries. Multiple vendors will sell different types of goods, and they may have their own union or a local government body to regulate and oversee operations. Each vendor has their own prices, supplies, reputation, and quantity. What if there was a marketplace for digital assets where users could act as buyers and sellers, setting their own prices and deciding how they want to trade their digital assets?
In brief, this type of marketplace eliminates the need for a middleman or overseer. As a result, users have the autonomy to decide which person to trade with, providing them with greater freedom. This analogy helps you to understand the key principles of Decentralized Exchanges (DEX). To own, trade, or buy a cryptocurrency, you must go to a cryptocurrency exchange. That’s where investors can convert their fiat money into cryptocurrency, and traders can sell their crypto assets.
As we said in the analogy, we can categorize exchanges according to the method of operation into two categories: centralized and decentralized.
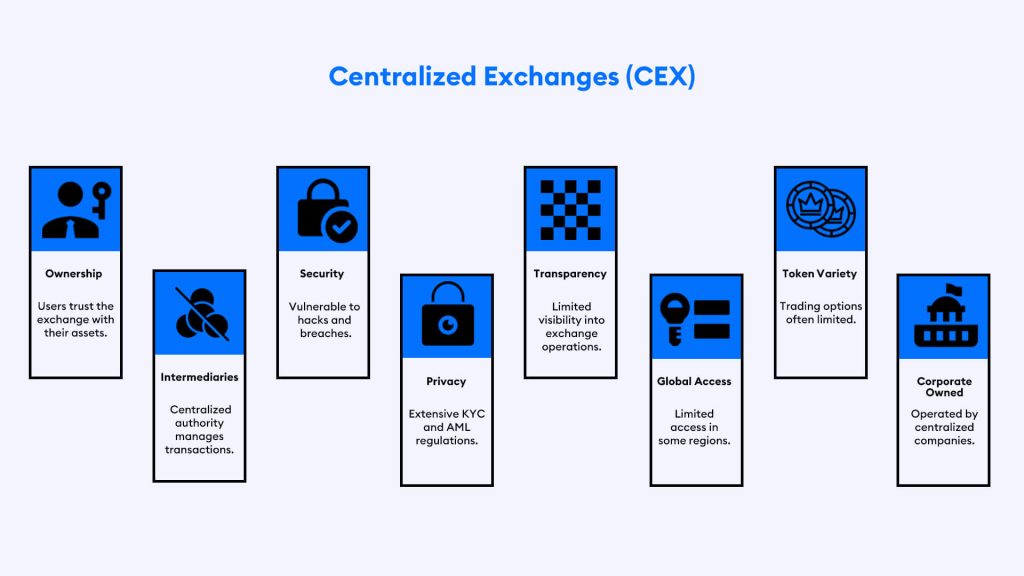
Centralized exchanges are monitored by a reliable third-party, requiring users to submit to processes such as Know Your Customer verifications, which must be completed prior to account registration; They have limitations on daily fund flow, usually with higher trading fees, our wallets are under their custody, and we can’t achieve anonymity. That’s where the decentralized exchanges or called DEX, come into play.
In this article, you will learn about the way DEXs operate, the differences between them, its benefits, risks and what the future holds for it.
What is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
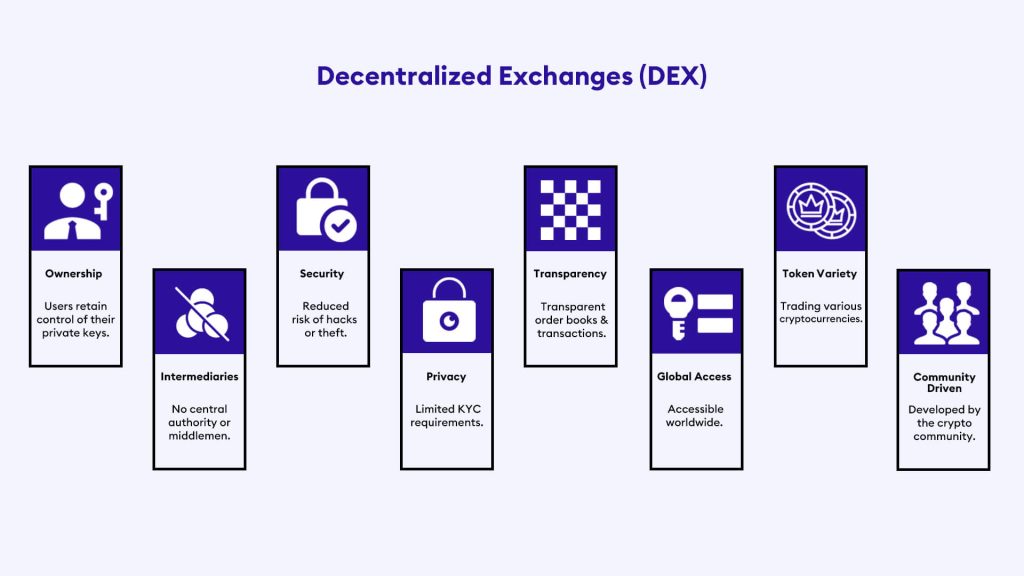
A decentralized exchange (DEX) is an online trading platform that does not rely on a centralized service to hold customers’ funds. Consequently, DEXs are not subject to the same regulations as centralized exchanges and do not have a single point of control.
Most decentralized exchanges are open-source projects that can be found on GitHub. Their aim is to create a fast, lightweight, and secure peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchange that anyone can use.
Instead of relying on central authorities, DEXs rely on smart contracts to facilitate user trades. For ease of understanding, smart contracts are self-executable agreements written in code. They don’t even need a central or cluster of servers to function. For example, when users want to trade one cryptocurrency for another, they can place an order on a DEX’s order book. DEX’s smart contract will then automatically match the order with another user wanting to trade the same cryptocurrencies.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are becoming increasingly popular with cryptocurrency traders due to the much lower transaction fees they charge compared to centralized exchanges. Another reason is that DEXs do not require users to deposit their funds in advance like centralized exchanges do, making them less vulnerable to hacking or theft. Furthermore, DEXs can be more attractive to users who value privacy and want to avoid censorship.
According to their operations and functionality, there are different types of DEXes: order book DEXs, Automated Market Makers, and DEX aggregators1.
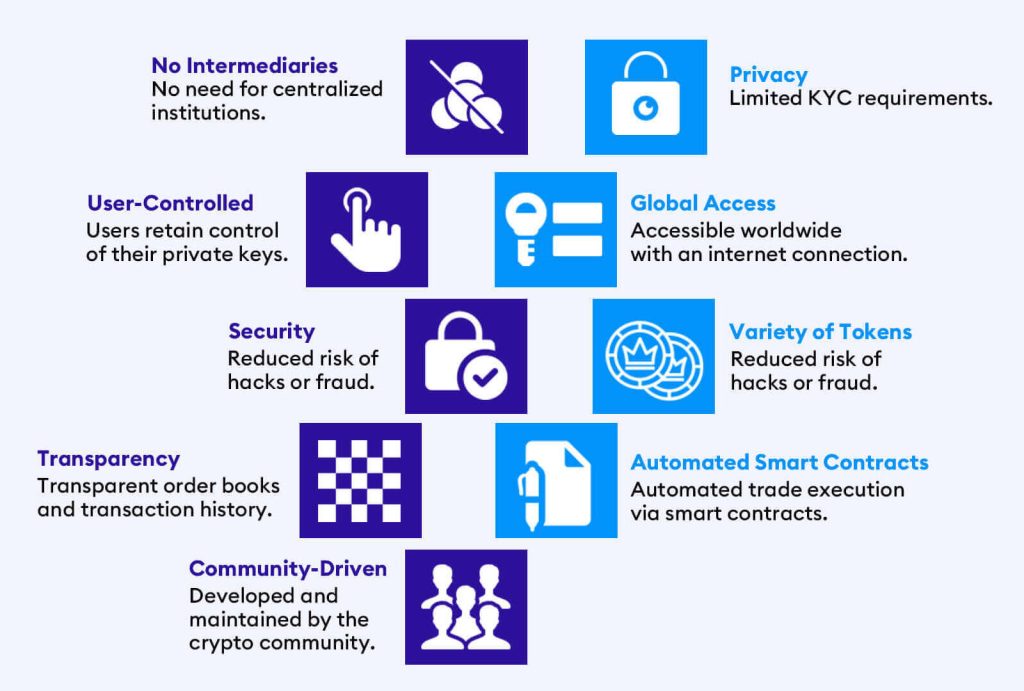
Why Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
Decentralized exchanges are quickly becoming commonplace in the world of cryptocurrencies. This new way of trading uses a network of nodes to store records of balances, trades, and transactions instead of relying on a single centralized authority.
There are many advantages of DEXs, but the main one is that they reduce the risk for users. Centralized exchanges are vulnerable to hacking and theft, leaving users with no recourse for their lost funds. Additionally, CEXs’ are increased privacy concerns as centralized exchanges require personal information.
Since DEXs use smart contracts to facilitate trades, which allows for greater anonymity and security compared to CEXs, users do not need to reveal their identity to trade on a DEX, and they retain complete control over their assets as these are stored on their personal wallets.
Altogether, people in this era have increased concerns for privacy, and the attractiveness of lower fees keeps drawing more people to DEXs.
Advantages of Using Decentralized Exchanges
- Security:
Decentralization and elimination of custody issues are possible since these platforms operate on a decentralized architecture, with no central authority controlling them. In contrast, centralized exchanges (CEXs) are controlled by a central entity, making them more vulnerable to hacks and security breaches and creating a single point of failure. Users don’t have to trust someone else with their security; they have complete control over it. In this way, DEXs reduce counterparty risks.2 - Greater control over funds:
In a DEX, users retain complete control over their assets as they are stored in their personal wallets, while in CEXs, records of assets are stored on a centralized server, which can be vulnerable to breaches. - Limitless range of tokens:
Compared to Centralized Exchanges (CEXs), newer cryptocurrency tokens are exclusively available on Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs). This is because regulated exchanges (“CEXs”) require tokens to pass specific regulations before they can be listed. These regulations must be met regardless of the utility potential of a coin, so all coins must go through some procedures before they become available on CEXs. However, in decentralized exchanges (DEXs), this can be done more efficiently. Thus, you can access a limitless range of tokens compared to a centralized exchange.
There is, however, a risk involved. With Ethereum-based tokens, anyone can launch their project without any vetting process. This means that it is essential to do research when considering investing in a particular project to ensure it is legitimate. (Be sure to do your research carefully!)
- No central point of failure like CEX:
DEXs are organized in a decentralized manner, making it difficult for local or global agencies to interfere with their functioning. The entire system remains unaffected if a fault occurs in one node or one endpoint is exposed to risk. - Innovative financial products:
Peer-to-peer lending, various DeFi services, anonymity, faster transactions, and relatively lower fees are only possible because of DEXs, something traditional financial bodies or even CEXs couldn’t offer. They allow users to trade directly with one another, opening up a wider pool of liquidity and potentially leading to better prices and faster trades.
Disadvantages or Potential Risks 3
While decentralized exchanges (DEXs) offer many advantages over centralized exchanges (CEXs), they also have some disadvantages and risks that you should consider as the consumer. Some of the main disadvantages and risks include the following:
- Poor user experience:
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) require a certain level of technical knowledge regarding blockchain technology and can be more challenging for new users to use than Centralized Exchanges (CEXs). In addition, their services, such as liquidity pools and exchange aggregators, and their different network names, such as ERC-20 and BEP-20, require a better understanding, making newbies a potential target for scammers. Trading on a decentralized exchange (DEX) is more complicated than centralized exchanges (CEX), involving more steps than just a few clicks. You must store your private keys securely since they cannot be retrieved once lost. Furthermore, avoid securing them in digital formats such as text or images. - Limited liquidity:
The order book and liquidity on DEXs are typically smaller than on CEXs, because of less popular among users. This may lead to less efficient price discovery and larger spreads. In addition, this can make it more difficult to find buyers or sellers for specific assets, especially for less popular tokens. - Limited options:
DEXs often come with a limited number of options when it comes to trading. Most useful options of CEXs, such as margin trading, stop loss, and lending, are not available inside. - No support or service:
Since they are decentralized, they are not expected to provide support for failed transactions or user accounts. At the end of the day, the user is fully responsible for his or her actions. This lack of user support may lead to users attempting too many requests after a failed attempt, which will directly affect the network’s responsiveness, speed, and scalability.
Decentralized Exchanges vs. Centralized Exchanges
Centralized exchanges have been the dominant form of cryptocurrency trading for years. They have been the most popular because they are easy to use and offer high liquidity. However, many decentralized exchanges now provide a different type of trading experience.
Decentralized exchanges are a new type of exchange that does not rely on a central intermediary to hold traders’ funds. Instead, trades happen directly between users (peer-to-peer) through an automated process called smart contracts. The result is faster transactions at a cheaper cost.
DEX operations are fully decentralized, and intelligent contracts facilitate its Peer-to-peer (P2P) trades. Smart contracts are another vast topic. The order books and their transactions will be carried out by peers or transaction participants. They are the ones that also control the fund flow of a user. DEXes doesn’t require the initial deposit and doesn’t hold the user’s fund (custodial way). Users can connect and trade directly with their existing wallet.
The decentralized nature of these exchanges means that they do not store any information about their users on centralized servers, which can be hacked or seized by authorities. This makes them more secure than centralized exchanges because traders do not need to provide personal information like their name or address for verification purposes in the name of filling out KYC. In addition, there is no single point of failure for hackers to target because data is distributed across the entire blockchain network.
In centralized exchanges, user data will be on their server, and users can get access to manage their funds by entering the email and password credentials of the exchange’s user account. These email and password combinations are easy targets for hackers and intruders. They benefit from it. Also, centralized exchanges rely on censorship. Cryptocurrencies are decentralized. They are supposed to be uncontrollable and not to come under legal bodies by authorities. Suppose a government announces that they are going to ban crypto-based investments; the first thing going to get banned is centralized exchanges because they must come under regulating bodies and legal supervision entities of each country.
The Future of Cryptocurrency Trading
The DEX trading platforms have been a surprise for many traders, as the idea of trading without any centralized authority had never been seen before. Therefore, when the mature audience and those who are aware of the pros and cons of this technology adopt it, it has the potential to revolutionize the industry.
The decentralized nature of these platforms means that no governing body or central entity can corrupt or control the flow of information. This also makes them more secure and less likely to be hacked.
It’s difficult to predict precisely what the future will hold for decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and trading, but here are a few potential developments that could shape the industry in the coming years.
- Improved Liquidity:
DEXs currently have lower liquidity than centralized exchanges (CEXs), making it harder for users to find buyers or sellers for specific cryptocurrencies at particular prices. However, DEXs may improve their liquidity through partnerships with CEXs or other liquidity providers. When this liquidity is expected to increase, DEX will gain a competitive advantage and can provide traders with better prices. - Greater Regulatory Clarity and its Development:
As the cryptocurrency market evolves, there is likely to be increased regulatory clarity around DEXs and other digital asset trading platforms. This could involve creating new laws and regulations specifically tailored to the unique characteristics of DEXs or applying existing regulations to the cryptocurrency industry. - Acting as a bridge to traditional finance:
It’s possible that DEXs will increasingly integrate with traditional financial systems, such as fiat currency and securities exchanges. This makes it easier for users to trade cryptocurrencies and other digital assets and brings additional liquidity to the market. The best example of this is Binance DEX.
Concluding Thoughts
The cryptocurrency market constantly evolves, and new technologies are continually being developed. Future DEXs will likely use many improved versions of emerging technologies such as DeFi, blockchain scaling solutions, stablecoins, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). These technologies could make DEXs more efficient and user-friendly and open up new trading opportunities. As the market matures and new technologies emerge, we will likely see a wide range of changes and developments shaping the industry’s future.
- What is a DEX? – #How Does a DEX work, Chain Link Artice “https://chain.link/education-hub/what-is-decentralized-exchange-dex”[↩]
- What is a DEX? “https://academy.binance.com/en/articles/what-is-a-decentralized-exchange-dex”[↩]
- Disadvantages and Potential Risks of DEX – 101 Blockchains: https://101blockchains.com/decentralized-exchanges-risks/[↩]


